We’re continuing on with our Geometry and Land Surveying theme today, following on from yesterday’s PHP and Javascript and CSS Shape Drawing Tutorial as shown below. When there are only small distances we talk about Plane Geometry because the curvature of the earth doesn’t come into the equation. When Earth curvature matters, over longer distances, in Land Surveying the term Geodetic Surveying is often used. Here, the equations used need to model the Earth as close as possible to known measurements.
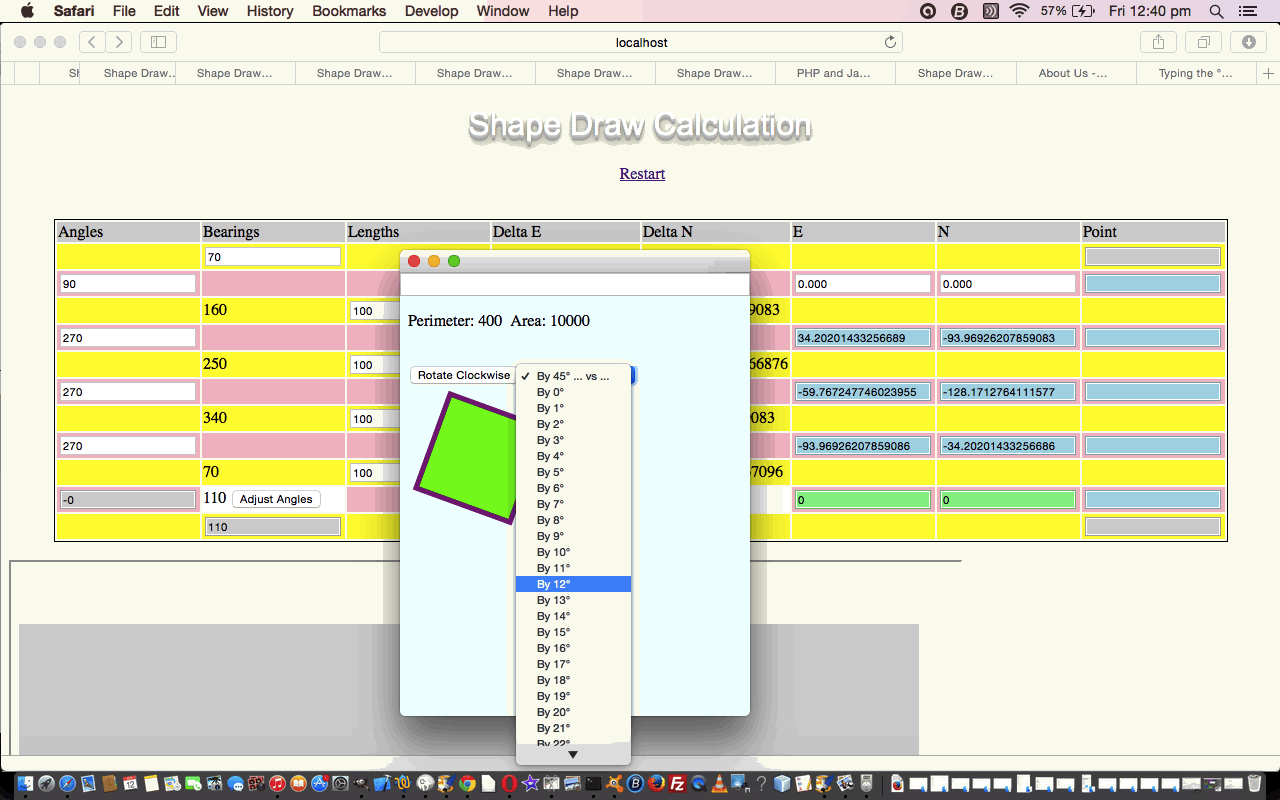
If you read yesterday’s posting you’ll see that we added some popup window functionality to display the Convex Polygon created by the web application in a relative sense, and to do this we called on (where variable “opop” is global in scope) …
opop = window.open("", "Polygon " + numlegs, "left=400,top=250,height=" + parseFloat(50 + maxy) + ",width=" + parseFloat(50 + maxx));
opop.document.write([someDerivedHTML]);
We’re here, today, to remind you, that that popup doesn’t have to be like a dead fish, just displaying information. It can be interactive itself, and is known to the “parent” window, so can have its own “hidden input” HTML element (for example) as per …
<input id="myunload" type="hidden" value=""></input>
… that is updated when a button as per (this function, that is used to create this button and a related dropdown) …
function buttonideas() {
var crotate1 = "<input type='button' onclick=' if (document.getElementById(\"myunload\") != null) { document.getElementById(\"myunload\").value=\"" + initiallength + "," + numlegs + "," + "\" + document.getElementById(\"myselect\").value; }' value='Rotate Clockwise'></input> <select id='myselect'><option value='" + eval(180.0 / numlegs) + "'>By " + eval(180.0 / numlegs) + "° ... vs ...</option></select>";
for (var steps=0; steps<=360; steps++) {
crotate1=crotate1.replace("</option></select>", "</option><option value='" + steps + "'>By " + steps + "°</option></select>");
}
return crotate1;
}
… then our “parent” window can swing into action via a setInterval() scenario (where variable sipos is global) …
sipos = setInterval(takealook, 5000);
… with code like …
function takealook() {
var things;
if (opop != null) {
if (opop.document.getElementById('myunload').value.indexOf(",") != -1) {
things = opop.document.getElementById('myunload').value.split(",");
opop.close();
opop = null;
if (things.length >= 3) {
if (sipos != null) { clearInterval(sipos); sipos = null; }
var bis = 0.0;
bis += parseFloat(initialbearing);
bis += parseFloat(things[2]);
window.location = "./ShapeDraw.php?sides=" + things[1] + ",0&length=" + things[0] + "&bearing=" + posval(bis);
}
}
}
}
… to allow for some HTML “svg” element rotation functionality, if the button is pressed, that is. One last nicety is to use the Window Event “onunload” to clear the setInterval handler with a web browser close or a user closing the parent webpage as per …
<body onunload=" if (sipos != null) { clearInterval(sipos); sipos = null; }" style="background-color: #fffff0;">
Link to Shape Draw live run (with Google Line Chart and HTML svg functionality) here.
Link to Shape Draw PHP source code ShapeDraw.php with changes from code yesterday as per this link.
You may be interested in CSS3 ways to rotate HTML elements as well, so we’ll leave you with this link to point you in the direction of where we have discussed this previously.
Previous relevant PHP and Javascript and CSS Shape Drawing Tutorial is shown below.
It is no coincidence that Geometry and Land Surveying have a lot in common. When there are only small distances we talk about Plane Geometry because the curvature of the earth doesn’t come into the equation. When Earth curvature matters, over longer distances, in Land Surveying the term Geodetic Surveying is often used. Here, the equations used need to model the Earth as close as possible to known measurements.
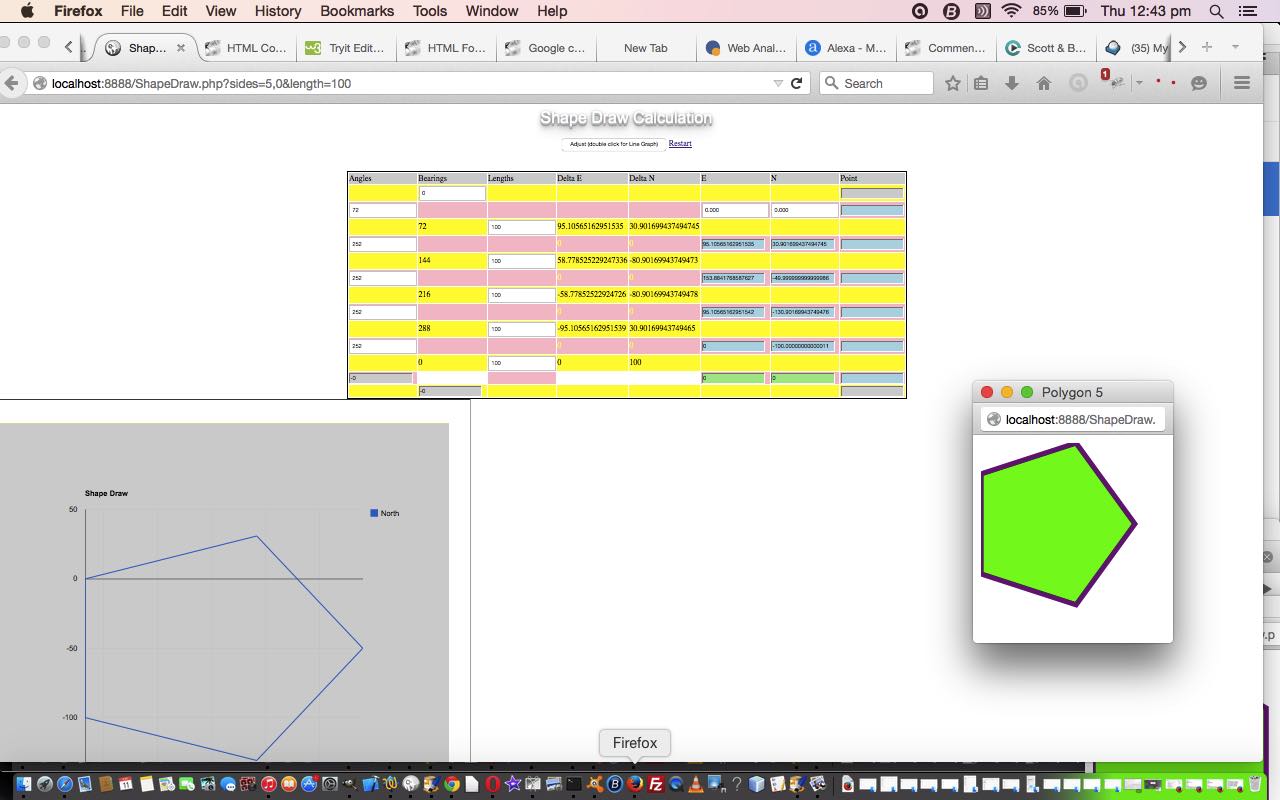
So today, with our Plane Geometry web application, we start with our previous Survey Traverse web application, and add to its functionality with ability for it to fill out more for the user to describe a regular polygon of their choosing, defined by …
- number of polygon sides
- length of each polygon side
We also add to the Google Charts Line Graph of the Drawn Shape a popup window showing the polygon as an HTML svg element. Part of the reason for this is that the Google Chart Line Graph can exaggerate the x or y co-ordinate of its plots, but with the HTML svg element, you avoid this issue, as we are just showing you a “relative” view of the shape (ie. as distinct from an “absolute” view with distinct co-ordinates).
The thinking here started with a look at New Century Maths stages 5.2/5.3 “Exterior angle sum of a convex polygon”. Did you know?
The sum of the exterior angles of a convex polygon is 360°.
What we found to be the case, practically speaking, to imagine the drawing of a regular even-sided convex polygon (with “numsides” sides) was …
- look north …
- turn clockwise (360° / numsides) for first line to draw (NB. there is more symmetry if this number is then divided by 2) … then from then on …
- off this previous line, turn clockwise (180° + (360° / numsides)) for subsequent lines
Link to Shape Draw live run (with Google Line Chart and HTML svg functionality) here.
Link to Shape Draw PHP source code ShapeDraw.php with changes from code below as per this link.
Hope you enjoy the geometry ideas, and will leave you with a very useful link that helped with the Convex Polygon method to calculate the Surface Area here.
Previous relevant HTML and Javascript and CSS Survey Traverse Tutorial is shown below.
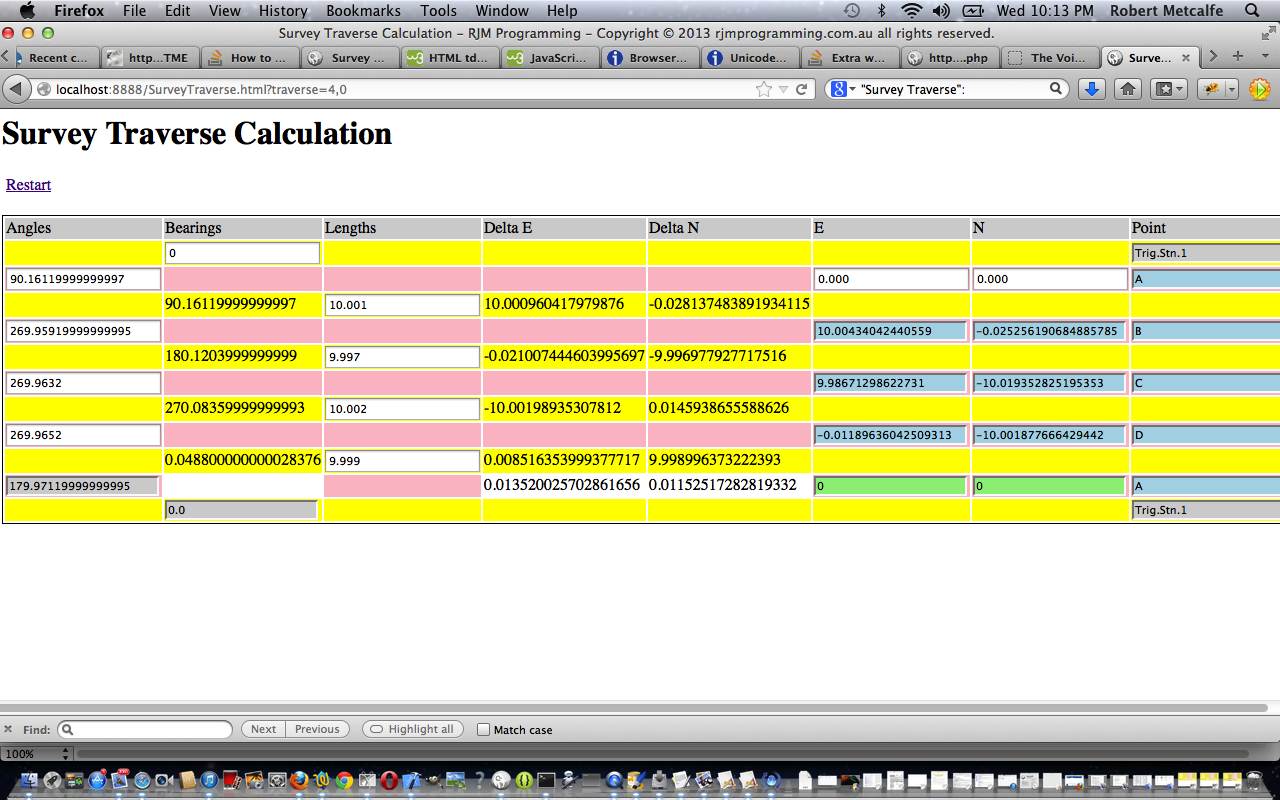
Here is a tutorial showing some client-side basics in HTML and Javascript and CSS all in the one HTML file, to simplify concepts. The tutorial subject matter is a webpage to perform Survey Traverse calculations. A Survey Traverse is:
Traverse is a method in the field of surveying to establish control networks.[1] It is also used in geodesy. Traverse networks involve placing survey stations along a line or path of travel, and then using the previously surveyed points as a base for observing the next point. Traverse networks have many advantages, including:
Less reconnaissance and organization needed;
While in other systems, which may require the survey to be performed along a rigid polygon shape, the traverse can change to any shape and thus can accommodate a great deal of different terrains;
Only a few observations need to be taken at each station, whereas in other survey networks a great deal of angular and linear observations need to be made and considered;
Traverse networks are free of the strength of figure considerations that happen in triangular systems;
Scale error does not add up as the traverse is performed. Azimuth swing errors can also be reduced by increasing the distance between stations.The traverse is more accurate than triangulateration[2] (a combined function of the triangulation and trilateration practice).[3]
Let’s see some simple HTML in action in a tutorial …
Link to HTML “spiritual home” … at W3Schools has many tutorials.
Link to Survey Traverse live run … here.
Link to Survey Traverse live run (additional Google Line Chart functionality) here.
Link to Survey Traverse information … from Wikipedia from which quote above comes.
Link to some downloadable HTML code … rename to SurveyTraverse.html which packages up a lot of Javascript and a little bit of CSS … or JaCvasScriptS … not sure whether this would ever catch on.
Link to some downloadable PHP programming code (additional Google Line Chart functionality) … rename to SurveyTraverse.php
If this was interesting you may be interested in this too.
If this was interesting you may be interested in this too.
If this was interesting you may be interested in this too.



15 Responses to PHP and Javascript and CSS Shape Rotation Tutorial