Working on yesterday’s Javascript Lazy Evaluation Follow Up Tutorial subject matter further today, we’d like to introduce a glossary of terms for beginners here …
- async
functionThe async function declaration creates a binding of a new async function to a given name. The await keyword is permitted within the function body, enabling asynchronous, promise-based behavior to be written in a cleaner style and avoiding the need to explicitly configure promise chains.
- await
operatorThe await operator is used to wait for a Promise and get its fulfillment value. It can only be used inside an async function or at the top level of a module.
- Promise
object (thenable)The Promise object represents the eventual completion (or failure) of an asynchronous operation and its resulting value.
- Lazy
syntax (function)Lazy evaluation means to delay the evaluation of an expression until it’s needed. Lazy evaluation is sometimes referred to as call-by-need.
The opposite of lazy evaluation is an eager evaluation. It’s an evaluation strategy used in most programming languages.
Lazy evaluation makes it possible to:
define potentially infinite data structures
increase performance by avoiding needless computations
customize iteration behavior for data structures that want its elements accessible to the public - setTimeout
function (global)The global setTimeout() method sets a timer which executes a function or specified piece of code once the timer expires.
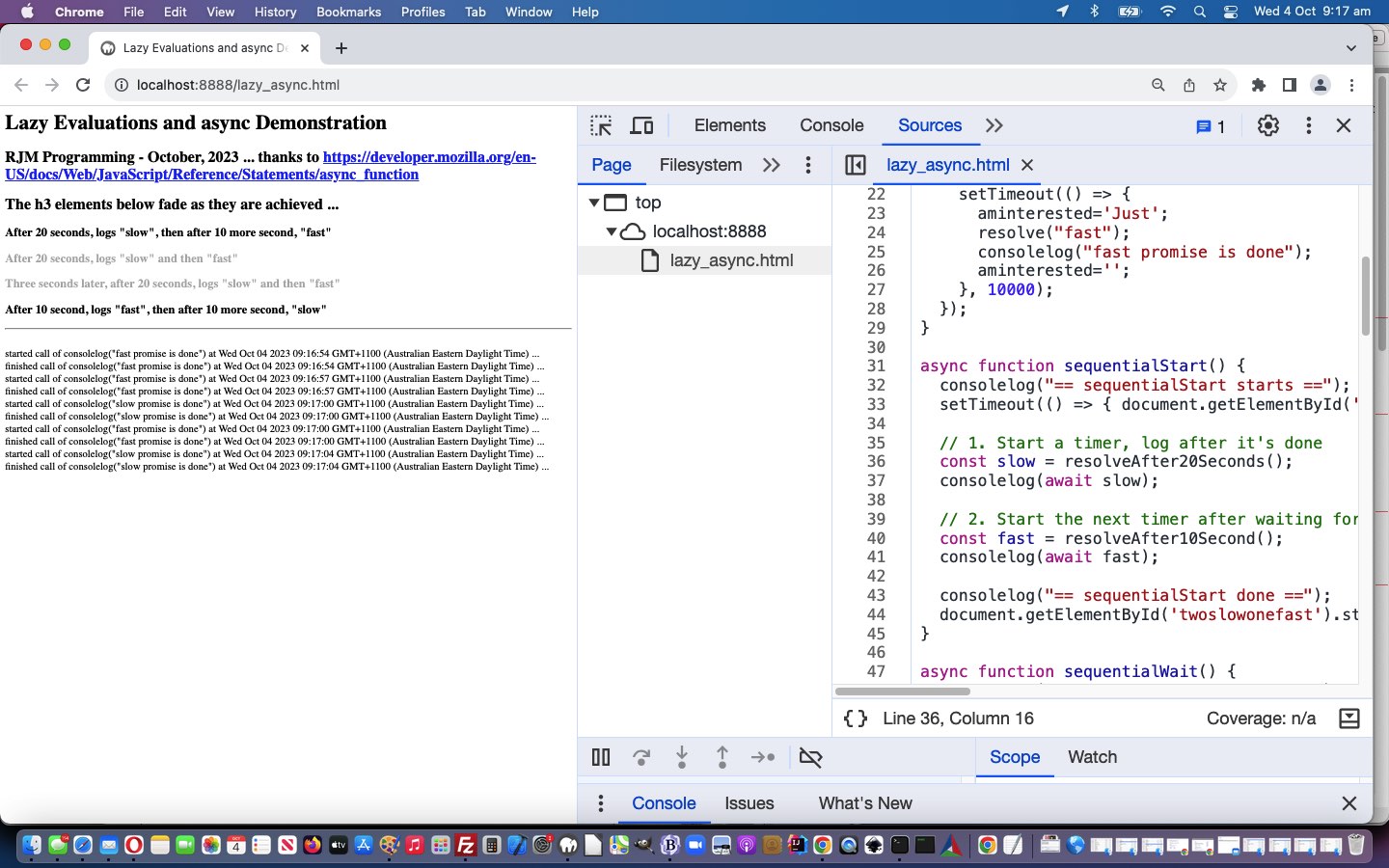
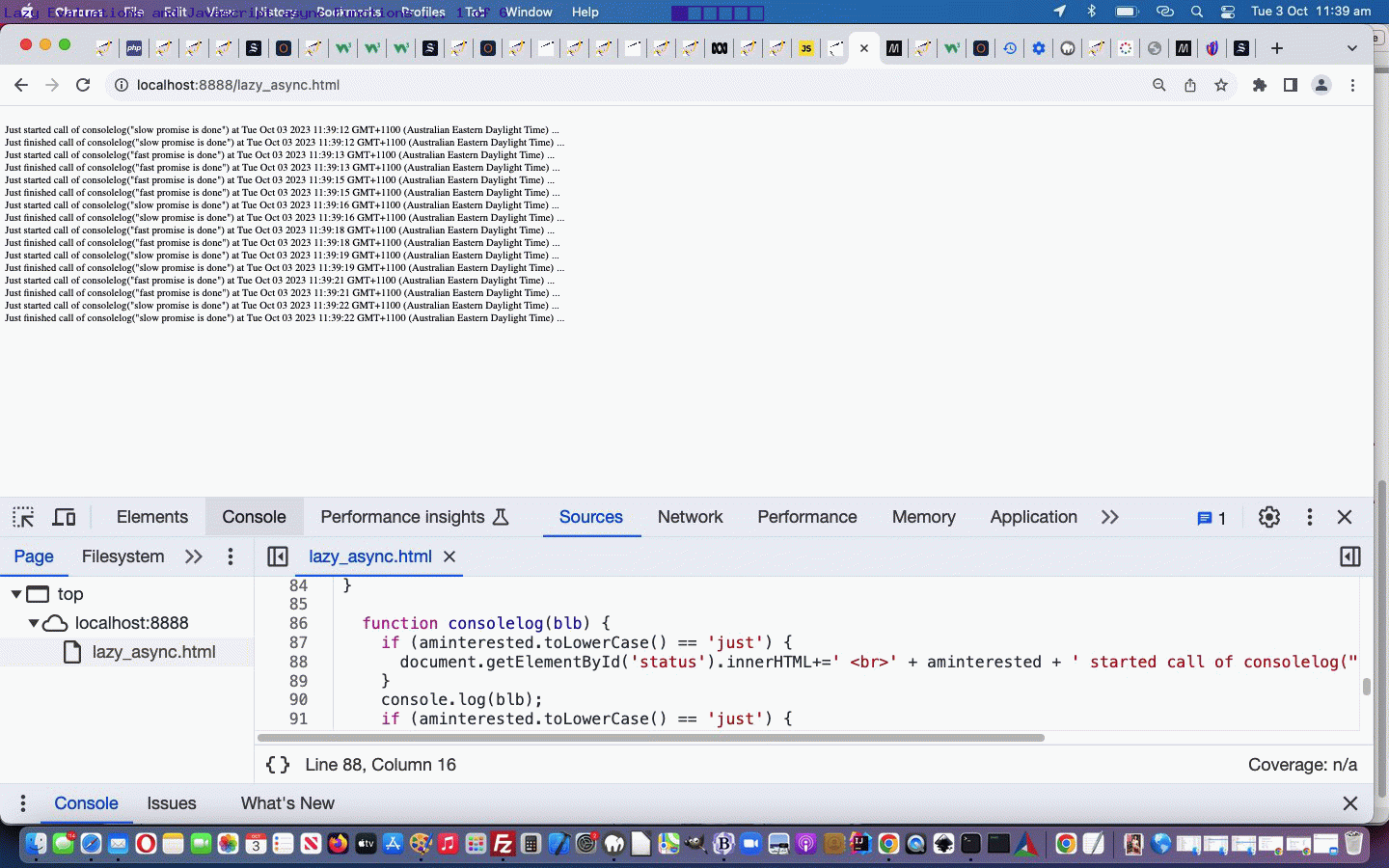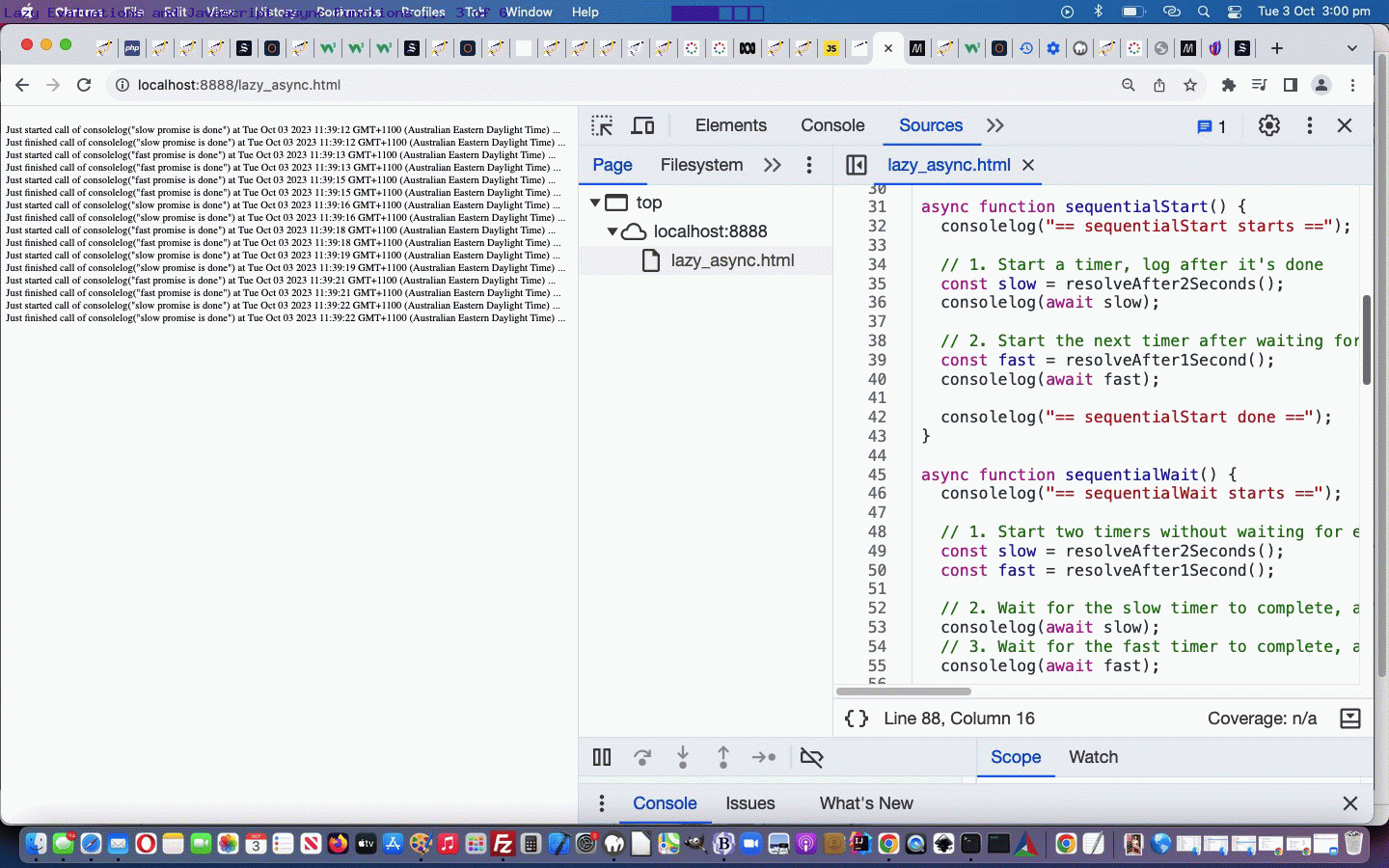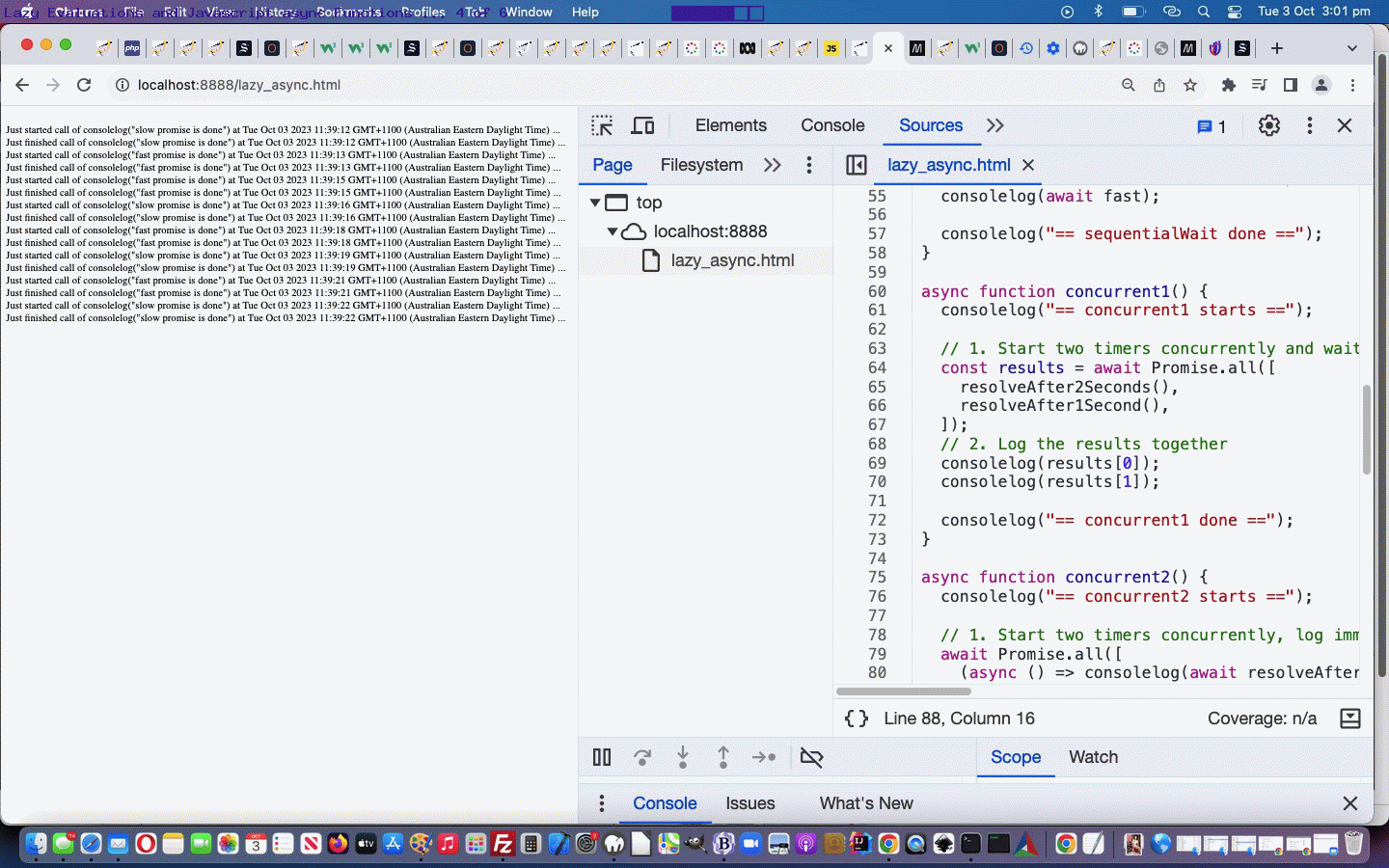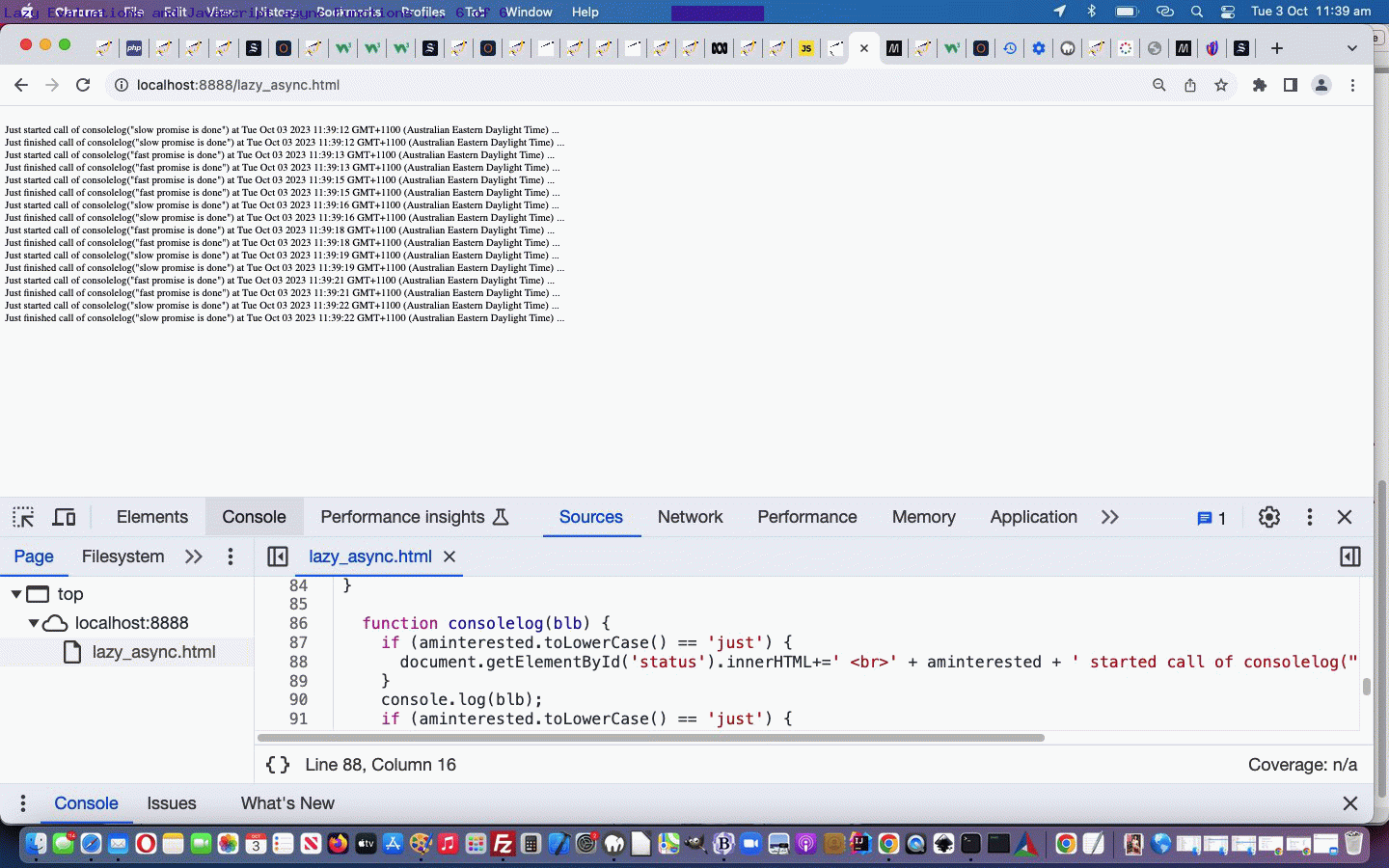
Meanwhile you can (re-)try our Javascript modified lazy_async.htm web application in a new tab or below …
Previous relevant Javascript Lazy Evaluation Follow Up Tutorial is shown below.
Further to yesterday’s Javascript Lazy Evaluation Primer Tutorial‘s subject matter regarding Lazy Evaluations and Javascript async functions, we’ve stumbled upon another great resource, thanks, from which we can base, to develop a web application, we’re hoping.
Within this “proof of concept” code basis you will find setTimeout (timer) references to Lazy Evaluations like …
setTimeout(() => {
aminterested='Just';
resolve("fast");
consolelog("fast promise is done");
aminterested='';
}, 1000);
… as a function that …
- attempts to start in one second’s time …
- as needed that function is performed
The possibilities here are multifaceted, and varied, and definitely worth experimenting with, within Javascript client work.
So our starting web application can be tried in a new tab or below …
Previous relevant Javascript Lazy Evaluation Primer Tutorial is shown below.
Do you remember, with the presentation of …
- Promise Object Sleeping and Doing Primer Tutorial we talked about the Javascript Promise object? Well today, in that similar line of thinking, we wanted to touch on …
- Lazy Evaluation in Javascript …
Lazy evaluation means to delay the evaluation of an expression until it’s needed. Lazy evaluation is sometimes referred to as call-by-need.
The opposite of lazy evaluation is an eager evaluation. It’s an evaluation strategy used in most programming languages.
Lazy evaluation makes it possible to:
define potentially infinite data structures
increase performance by avoiding needless computations
customize iteration behavior for data structures that want its elements accessible to the public
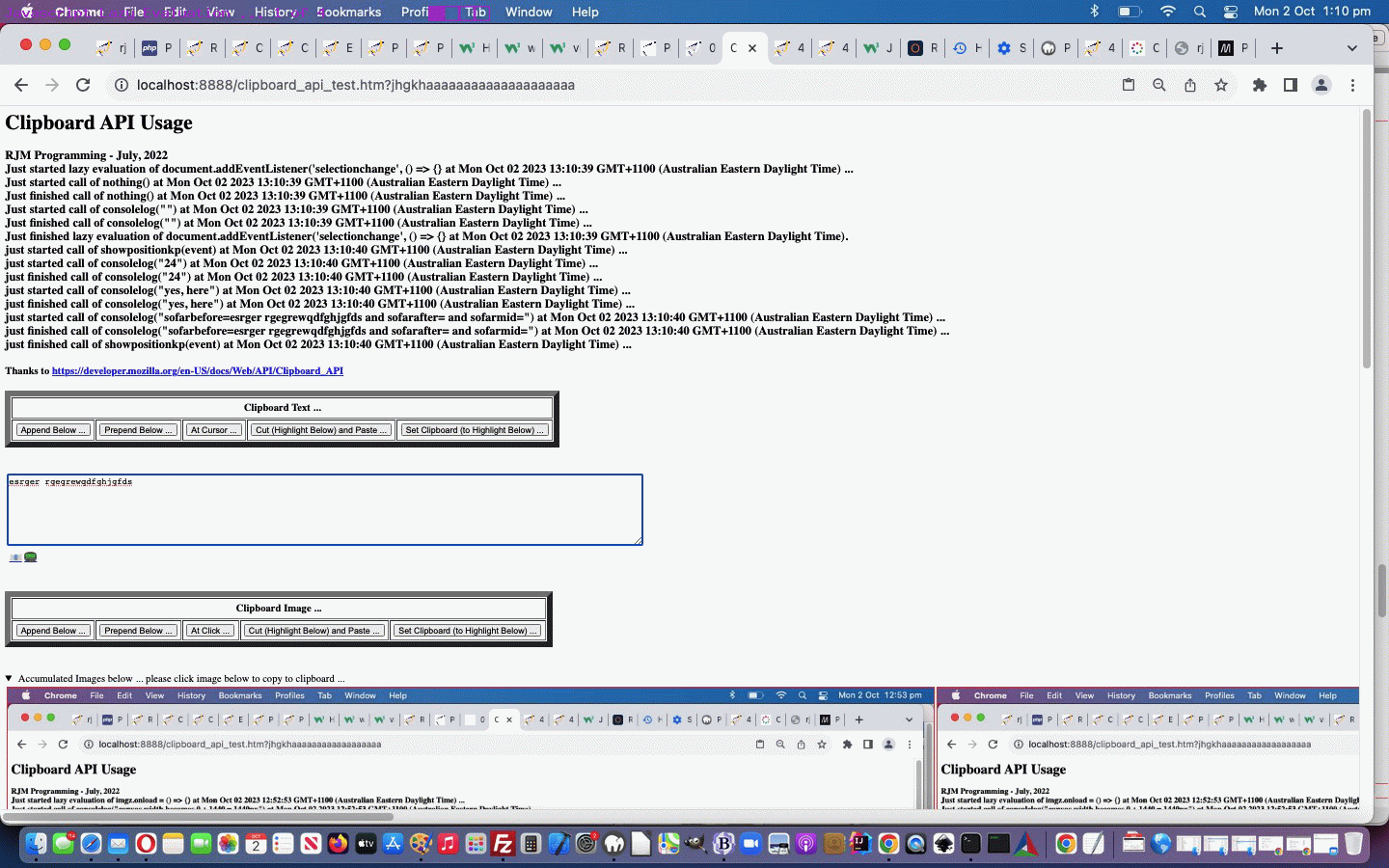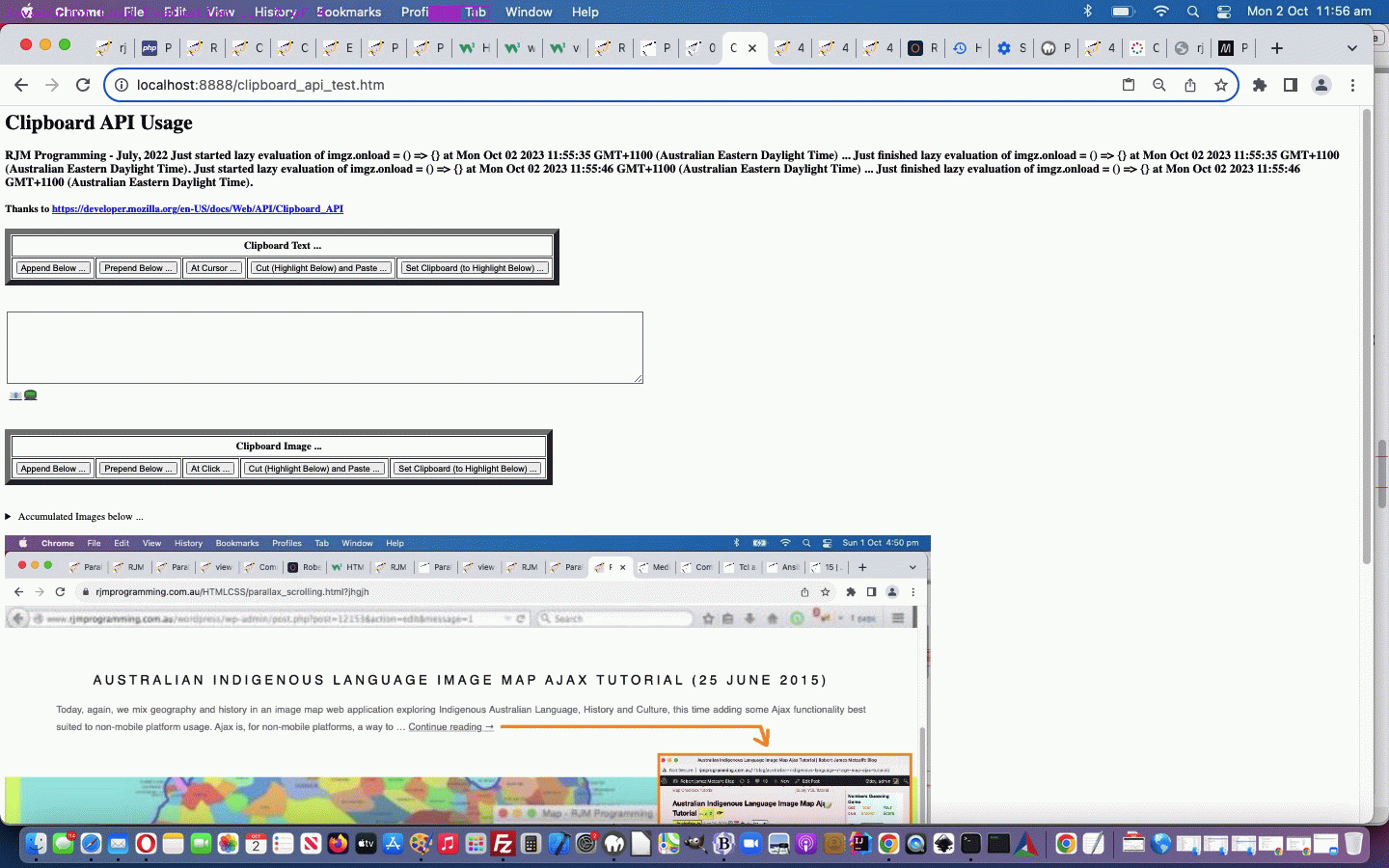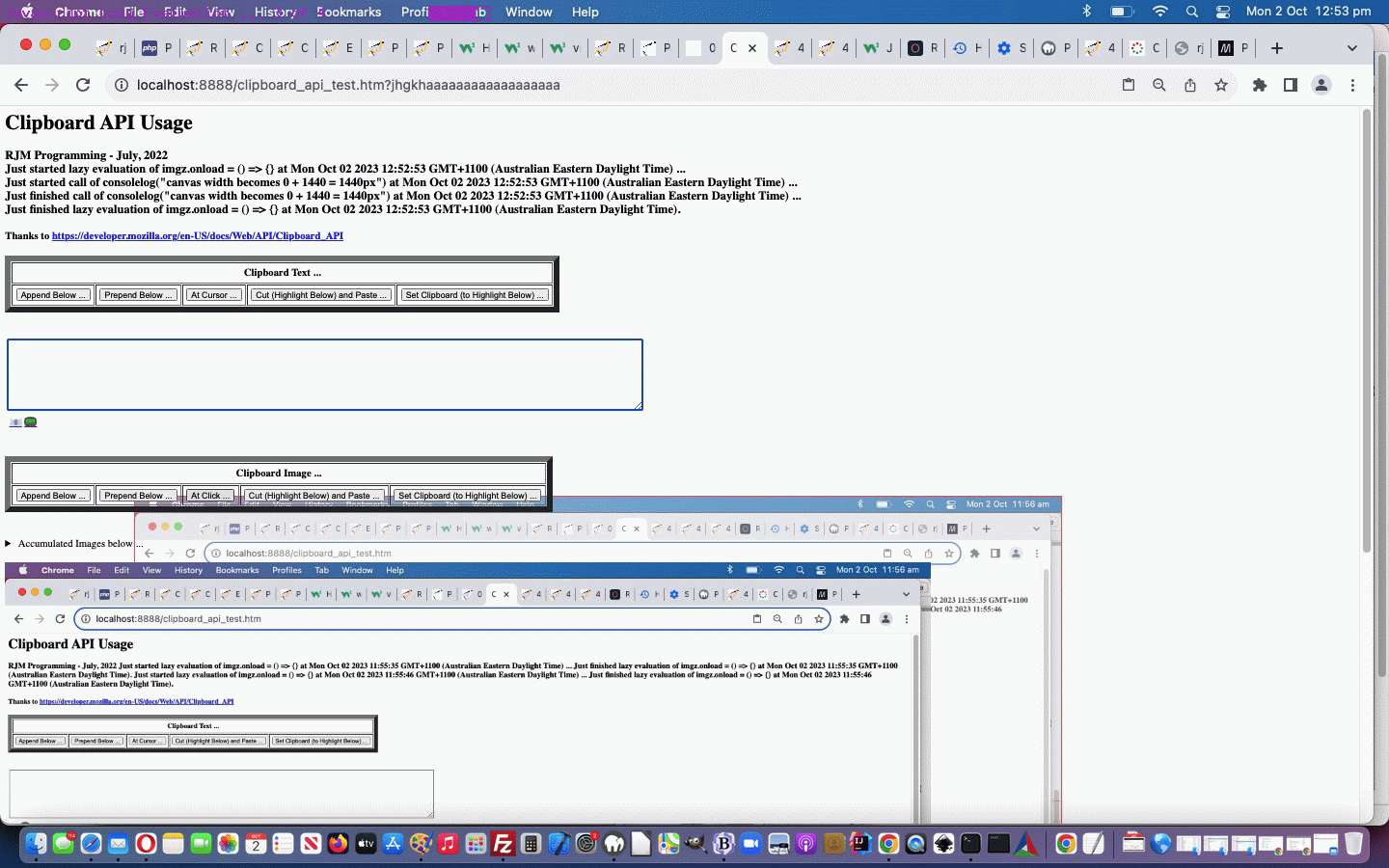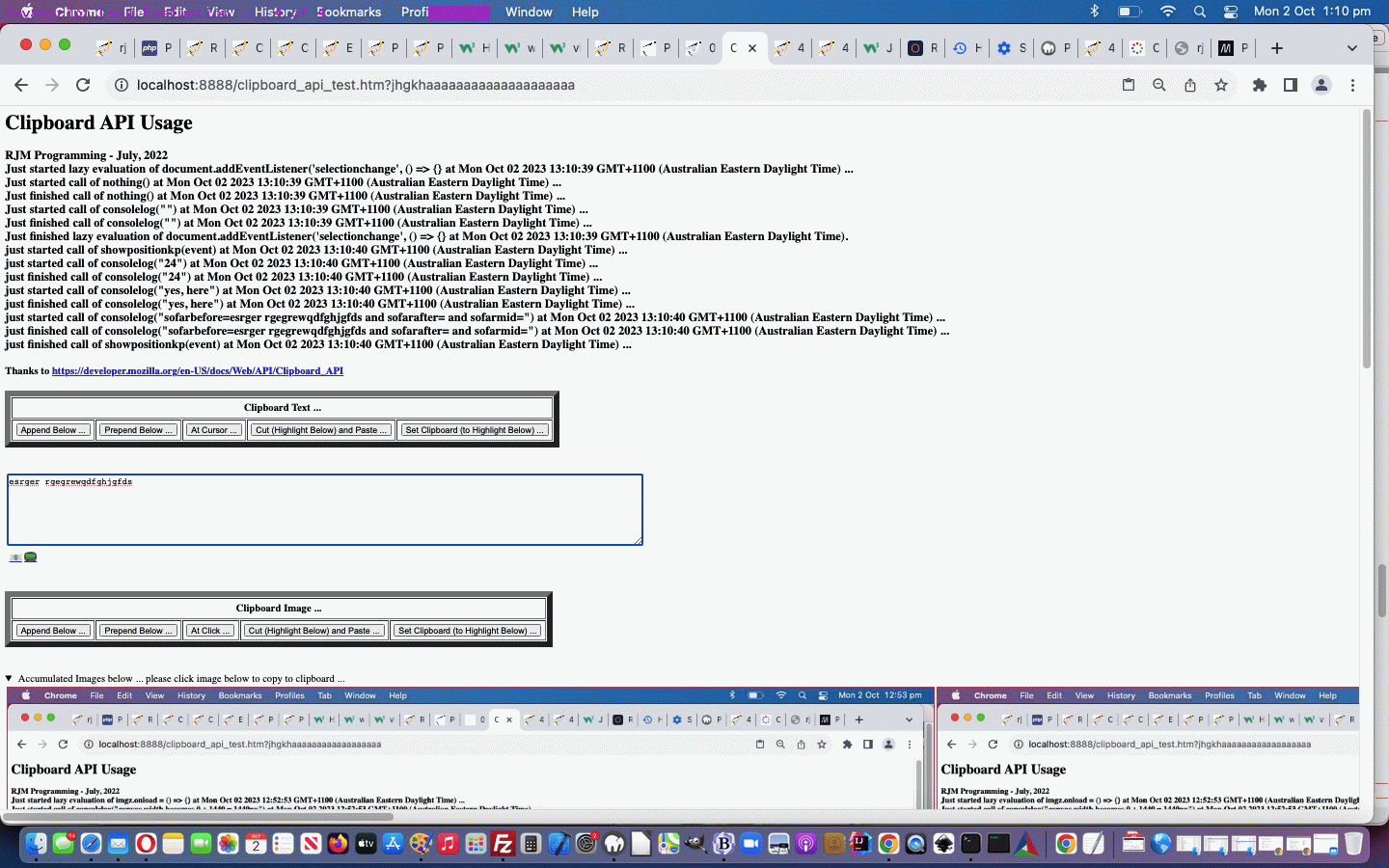
Personally, we’re more your “eager” types, but we’ve had help in the past from brilliant “lazy” types too, especially when we presented Selection API and Clipboard API Tutorial, and so, we honed in on some Javascript “Lazy Evaluation” code, and put together some status information shown regarding timings and calls with respect to Javascript …
- “Lazy Evaluation” in Javascript … classical syntax goes …
f = () => expression;
… and … - async function in Javascript … classical syntax example goes …
function resolveAfter2Seconds() {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('resolved');
}, 2000);
});
}
async function asyncCall() {
console.log('calling');
const result = await resolveAfter2Seconds();
console.log(result);
// Expected output: "resolved"
}
… into the changed clipboard_api_test.html Selection and Clipboard API usage web application for you to try yourself with some image or text clipboard usages.
Previous relevant Promise Object Sleeping and Doing Primer Tutorial is shown below.
We’re here today to fulfil yesterday’s Web Application Controlled Progress Cursor Primer Tutorial‘s pledge …
… which reminded me that we need to learn some more about the promise object
… and were happy to discover the Promise object talents of …
- sleeping … allowing for …
- multitasking
- doing … all using clientside Javascript
… very interesting. The serverside languages such as PHP make it a doddle to multitask (via sleep) but Javascript sleep has not always been a straightforward proposition, until we could promise, that is!
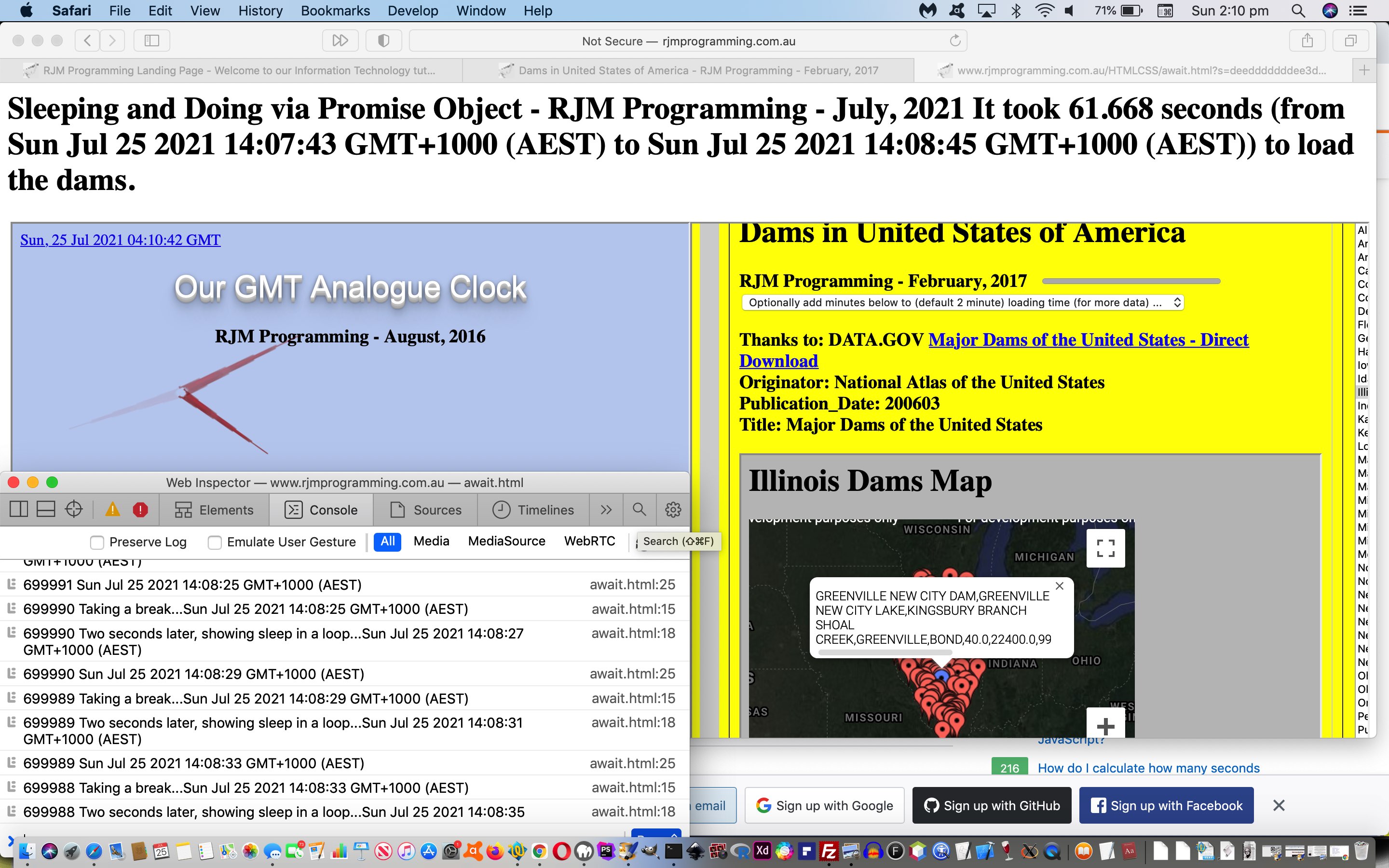
Today’s await.html‘s use of it to sleep and in between show …
- analogue clock … and …
- Dams of the USA (via dams_usa.html changed this way)
… asynchronously both doing their own thing while the await.html works away in the background too, feeding off “child 2” clicks of “child 1” above to know when to say how long the dams took to load. Yes, the “child 2” “onload” event, alone, cannot help determine this, but more “drilling into” the inner workings of the code behind “child 2″‘s progress element, via …
<html>
<head>
<script type='text/javascript'>
var numsleeps=700000;
var ix=0;
var d=new Date();
var marks=[new Date(), new Date()];
var imark=0;
function sleep(ms) { // thanks to https://stackoverflow.com/questions/951021/what-is-the-javascript-version-of-sleep
return new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, ms));
}
async function demo() {
console.log(numsleeps + ' Taking a break...' + d);
await sleep(2000);
d=new Date();
console.log(numsleeps + ' Two seconds later, showing sleep in a loop...' + d);
// Sleep in loop
for (let i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
if (i === 3) {
await sleep(2000);
d=new Date();
console.log(numsleeps + ' ' + d);
}
}
numsleeps--;
if (('' + numsleeps) != '0' && ('' + numsleeps).indexOf('-') == -1) { setTimeout(demo, 1); }
}
function betw() {
var seconds = (marks[1].getTime() - marks[0].getTime()) / 1000;
document.getElementById('sh1').innerHTML='It took ' + seconds + ' seconds (from ' + marks[0] + ' to ' + marks[1] + ') to load the dams.';
numsleeps=0;
}
function markit() {
marks[imark]=d;
imark++;
console.log('mark ' + imark + ': ' + d);
if (imark == 2) { setTimeout(betw, 800); imark=0; }
}
demo();
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Sleeping and Doing via Promise Object - RJM Programming - July, 2021 <span id=sh1></span></h1>
<table style=width:100%;height:90%;><tr><td><iframe onclick="markit();" id=lif src=./analogue_clock.htm style=width:100%;height:100%;></iframe></td><td><iframe id=rif src=./dams_usa.html?rand=7564675 style=width:100%;height:100%;></iframe></td></tr>
</body>
</html>
Previous relevant Web Application Controlled Progress Cursor Primer Tutorial is shown below.
We had occasion to revisit the card game (and more) recent web application exploits highlighted in the recent Just Javascript Card Game Cursor Tutorial thread of blog postings and shaped to play Bridge via …
https://www.rjmprogramming.com.au/HTMLCSS/cards_usefocus.html?card_memories=04.1:ara
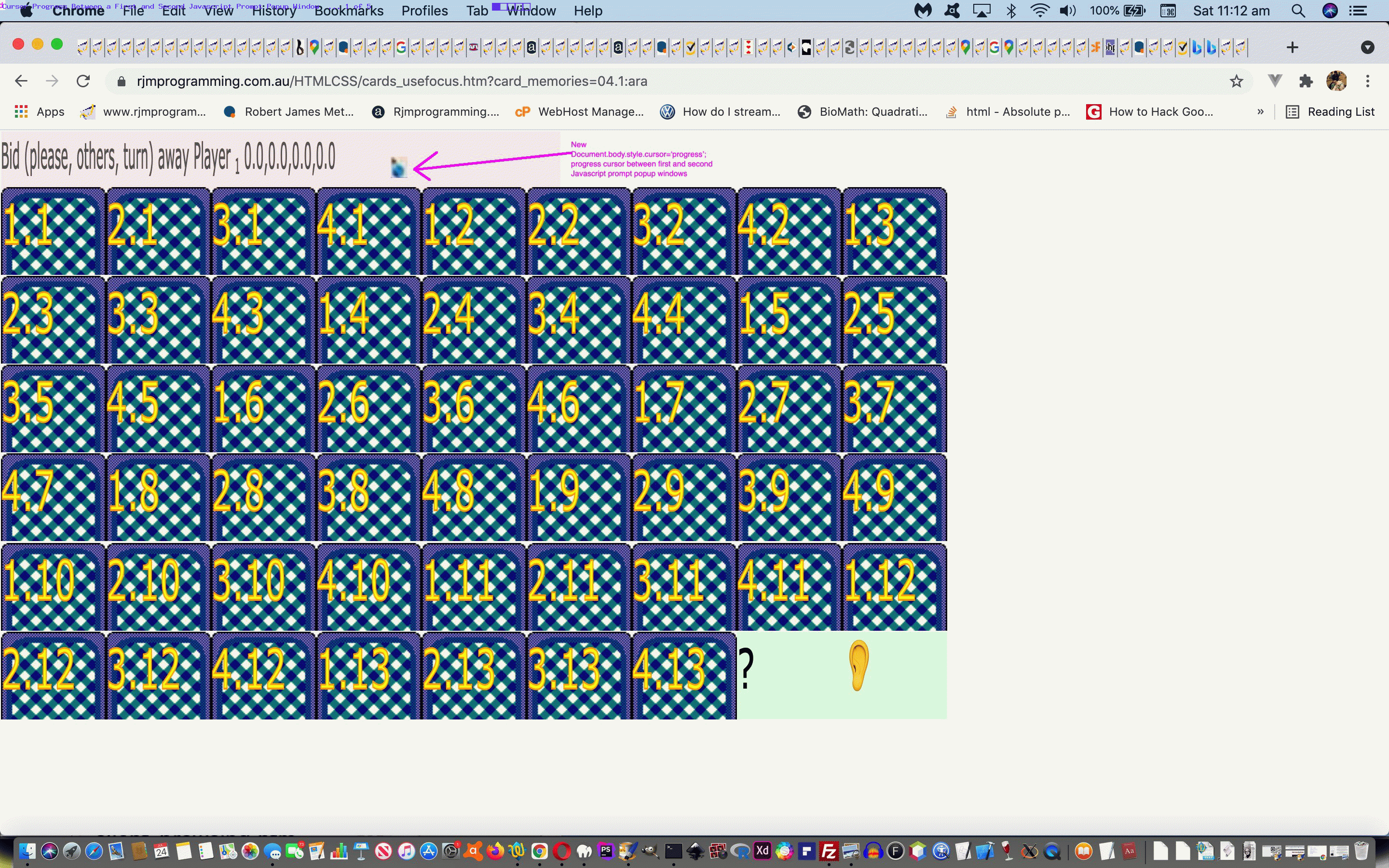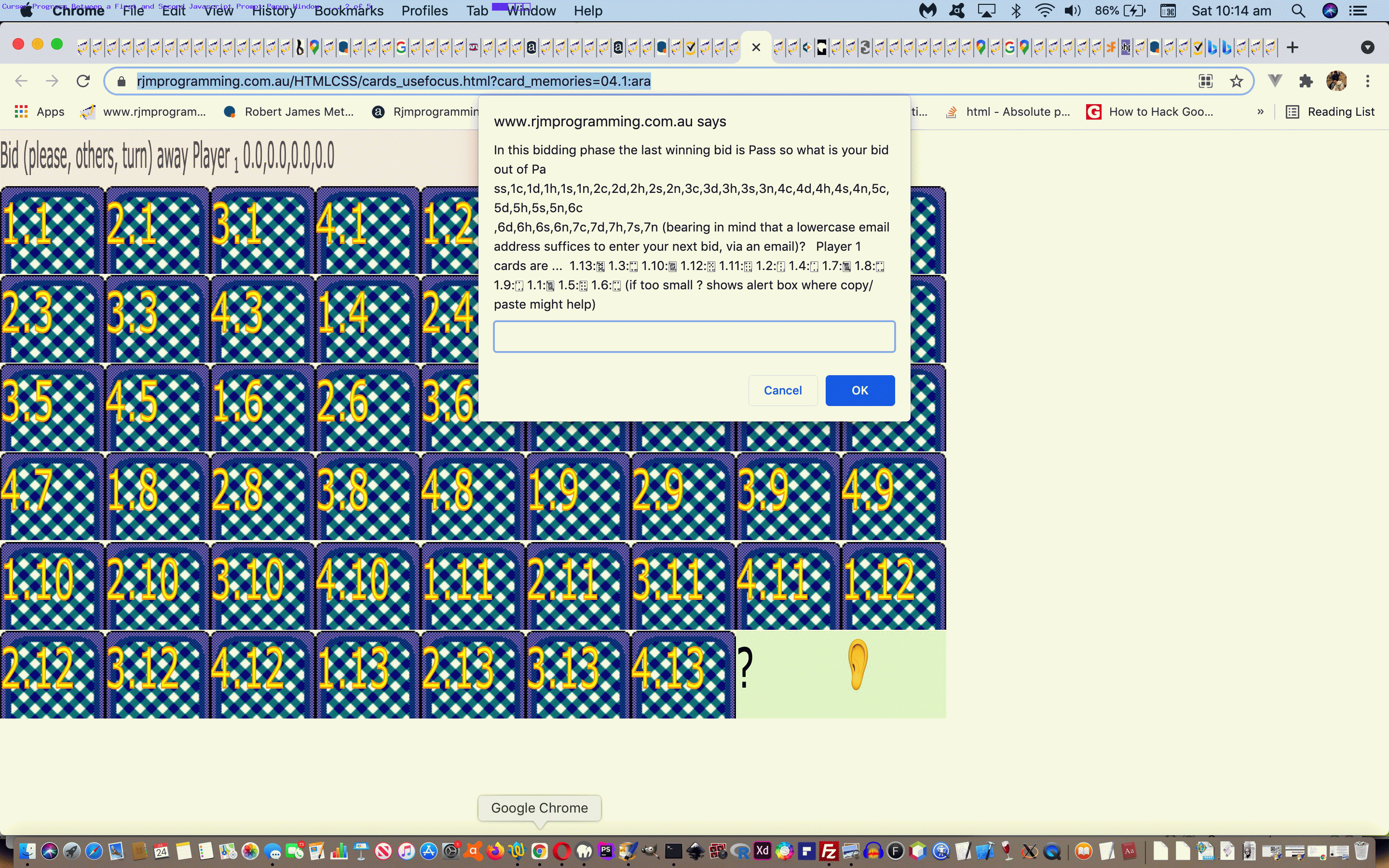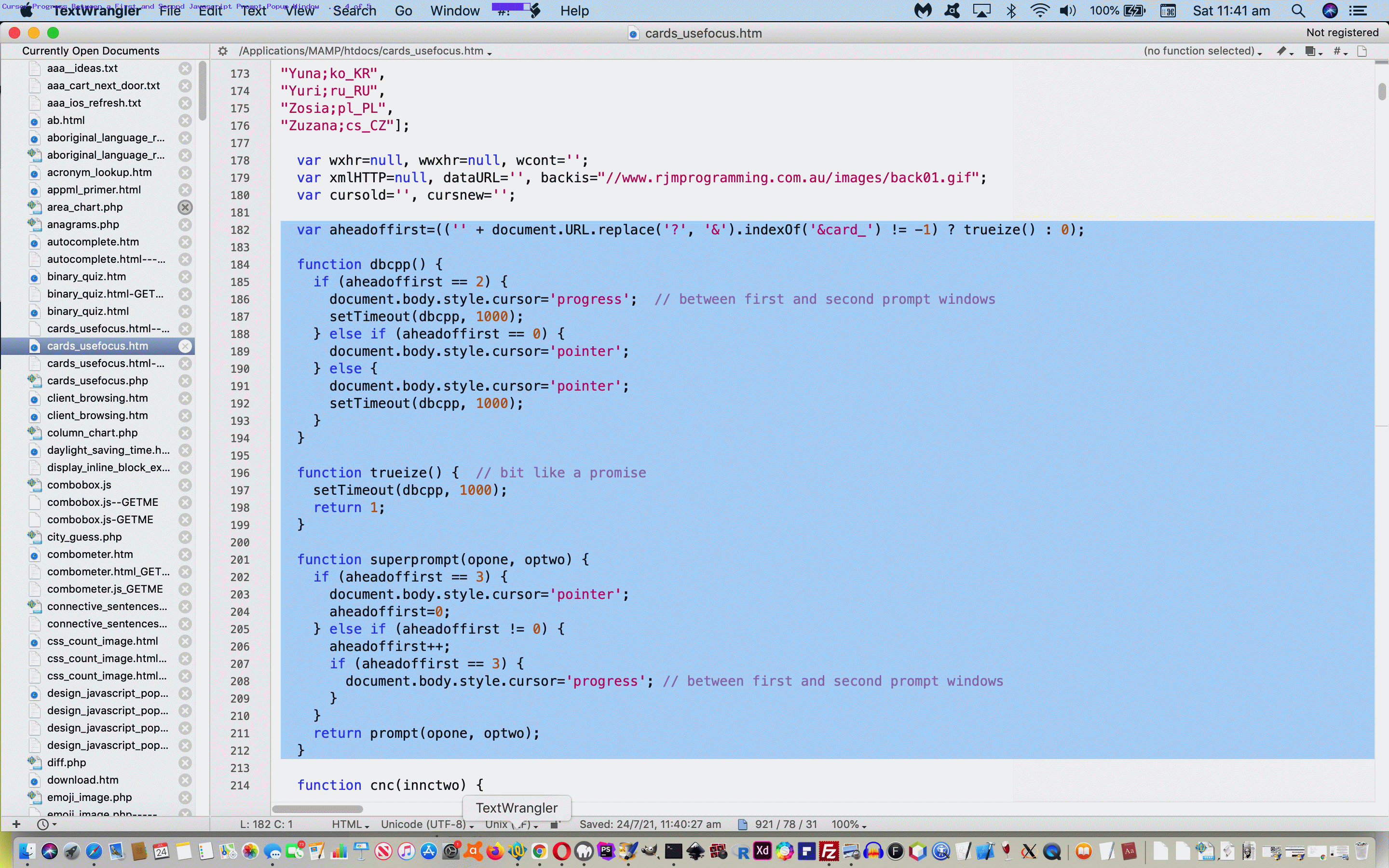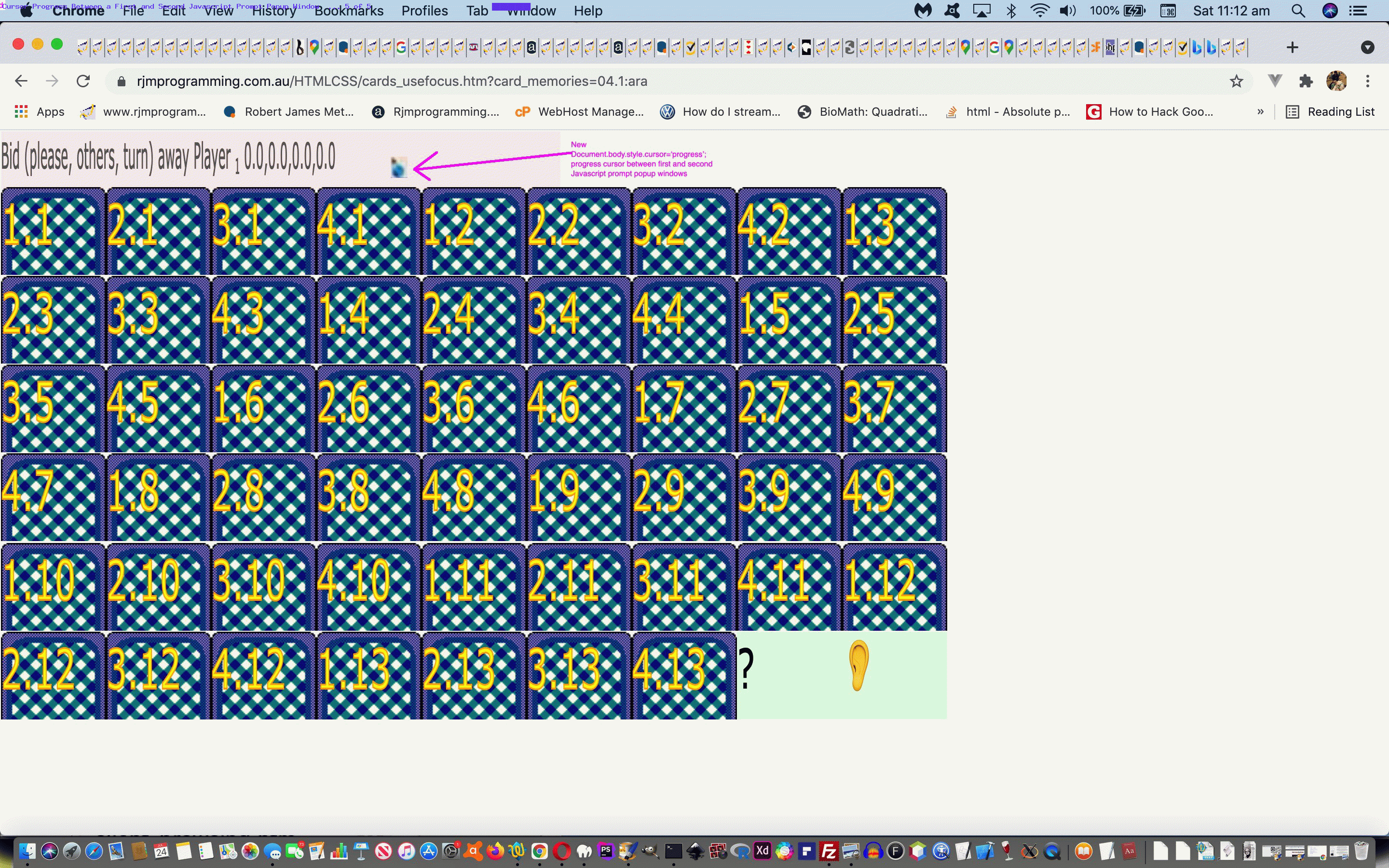
… and was “personally relatively” happy up to the first Javascript prompt popup window. Huh?! What’s with “personally relatively”? Can I be serious? Well, I’m insulted!
The thing is, I don’t mind, when I’m writing the code (funny about that?!) very complex and convoluted prompt window instructions and options. But …
- not everybody is willing to read such long diatribes
- actions can speak louder than words, so we figure between those first two prompt windows in a Bridge or 500 card game, it would be beneficial to show a “progress cursor” (ie. usually associated with the user waiting for a process to finish) between the first and second prompt windows to help show the players there could be waiting and irrelevant players turning away should all four players want to play fairly in their game
It was an interesting Javascript coding exercise …
- (sort of) overload the “prompt” function with our inhouse “superprompt” function via …
- globally replace ” prompt(” with ” superprompt(“
- globally replace “=prompt(” with “=superprompt(“
- add the following Javascript code …
var aheadoffirst=(('' + document.URL.replace('?', '&').indexOf('&card_') != -1) ? trueize() : 0);
function dbcpp() {
if (aheadoffirst == 2) {
document.body.style.cursor='progress'; // between first and second prompt windows
setTimeout(dbcpp, 1000);
} else if (aheadoffirst == 0) {
document.body.style.cursor='pointer';
} else {
document.body.style.cursor='pointer';
setTimeout(dbcpp, 1000);
}
}
function trueize() { // bit like a promise
setTimeout(dbcpp, 1000);
return 1;
}
function superprompt(opone, optwo) {
if (aheadoffirst == 3) {
document.body.style.cursor='pointer';
aheadoffirst=0;
} else if (aheadoffirst != 0) {
aheadoffirst++;
if (aheadoffirst == 3) {
document.body.style.cursor='progress'; // between first and second prompt windows
}
}
return prompt(opone, optwo);
}
… which reminded me that we need to learn some more about the promise object.
See this in action with the changed cards_usefocus.html code behind the “Just Javascript” Memories Card Game or live run with single window (good for mobile) or default live run (for your platform, and if non-mobile it will try child popup windows).
If this was interesting you may be interested in this too.
If this was interesting you may be interested in this too.
If this was interesting you may be interested in this too.
If this was interesting you may be interested in this too.
If this was interesting you may be interested in this too.