As a programmer, as time goes on, I get the creeping feeling that more is being asked of our job description. Pretty sure am not alone, and hope world employment is not going to be too hard hit by similar such “pushes”. Thinking on it, though, what would we expect to happen if robotics seriously became more “real”? Don’t think it takes a Nostrodamus futurist to have predicted: ‘Programmers would be drawn more into the “modelling” of systems and “deployment”.’
So what is great for a project’s “bottom line” would be …
- a programmer doesn’t lose their expertise in programming and unit testing, as their primary “length of time” focus … yet …
- being as the programmer is there “in amongst it” can they help model the (customer) system, help model it, and program in that modelled environment prior to redeployment, even if they are not directly responsible for any of the “out of office” parts of setting this modelling up (ie. things are like “in the old days” for the programmer geographically speaking (or more convenient, actually), but the modelling means it is like they are in two places at the same time, but not interfering in the operations of that second (customer) environment)? … oh and yes, that “modelling” is simple enough not to spend days upon days attending to it … and yes, one last thing, that on the next similar such project, the knowledge from the previous one’s workings is incorporated almost seamlessly into the next?
… and, trying not to overstate all this too much, but deployment with software tools such as Ansible makes all the above possible for (programmer) people whose strength is not exactly “deployment” or “configuration management”.
The reason to try to not overstate all this is that Ansible is based on very simple principles … “Ansible is masterless and it uses SSH as its primary communication layer.”.
Today we’re picking up from where we left off with the last advice from Ansible Hello World Primer Tutorial from two days ago (we studied Vagrant Primer Tutorial yesterday) …
In the meantime, research into Ansible Playbooks would be a great idea.
Specifically we’re going to meander along through the actions advised in Chapter 2 (“Playbooks: A Beginning”) of “Ansible Up and Running” by Lorin Hochstein … just in case you haven’t done this yourself.
Ansible Hello World Primer Tutorial left us with a Vagrantfile …  … that becomes
… that becomes  … to expose ports 80 and 443 in order to access them, and that requests to ports 8080 and 8443, respectively, are forwarded to 80 and 443 on the Vagrant (Oracle VM VirtualBox) machine … so that …
… to expose ports 80 and 443 in order to access them, and that requests to ports 8080 and 8443, respectively, are forwarded to 80 and 443 on the Vagrant (Oracle VM VirtualBox) machine … so that …
vagrant reload
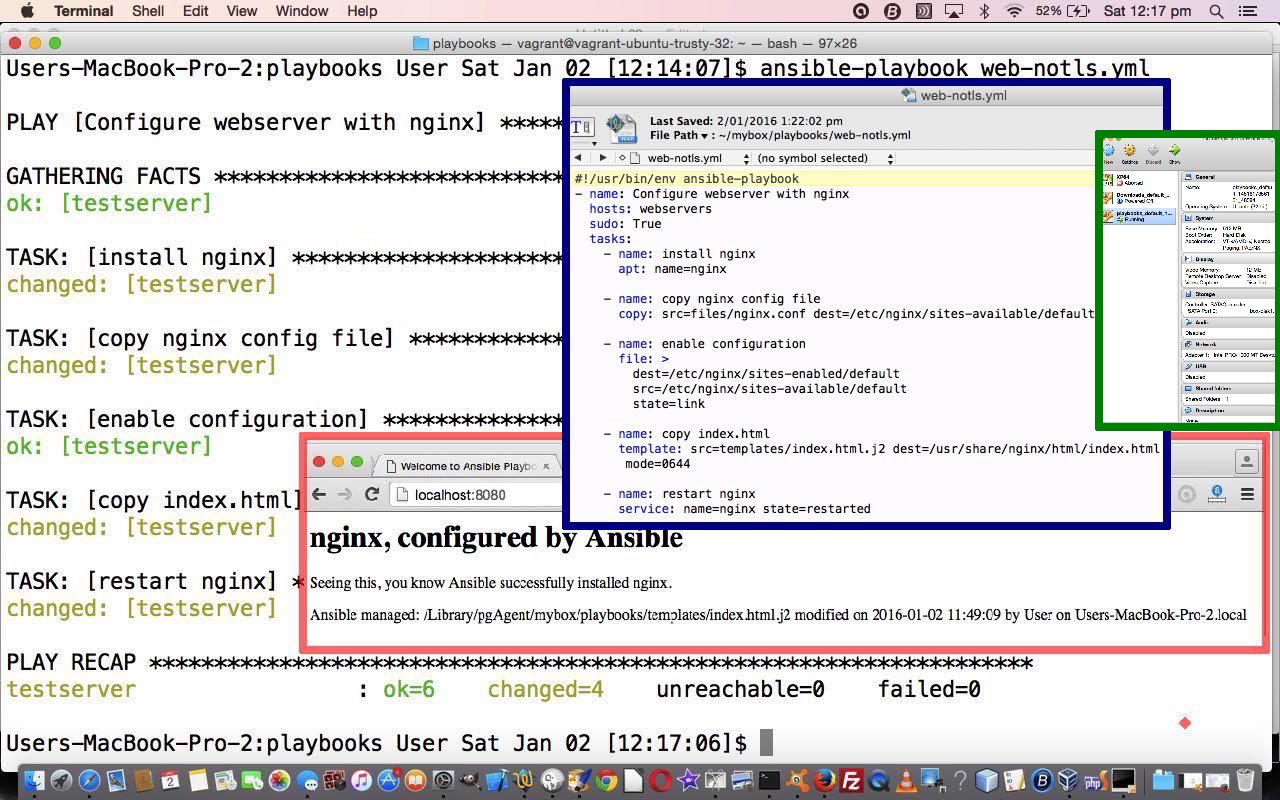
… you could call Vagrantfile … looks like … 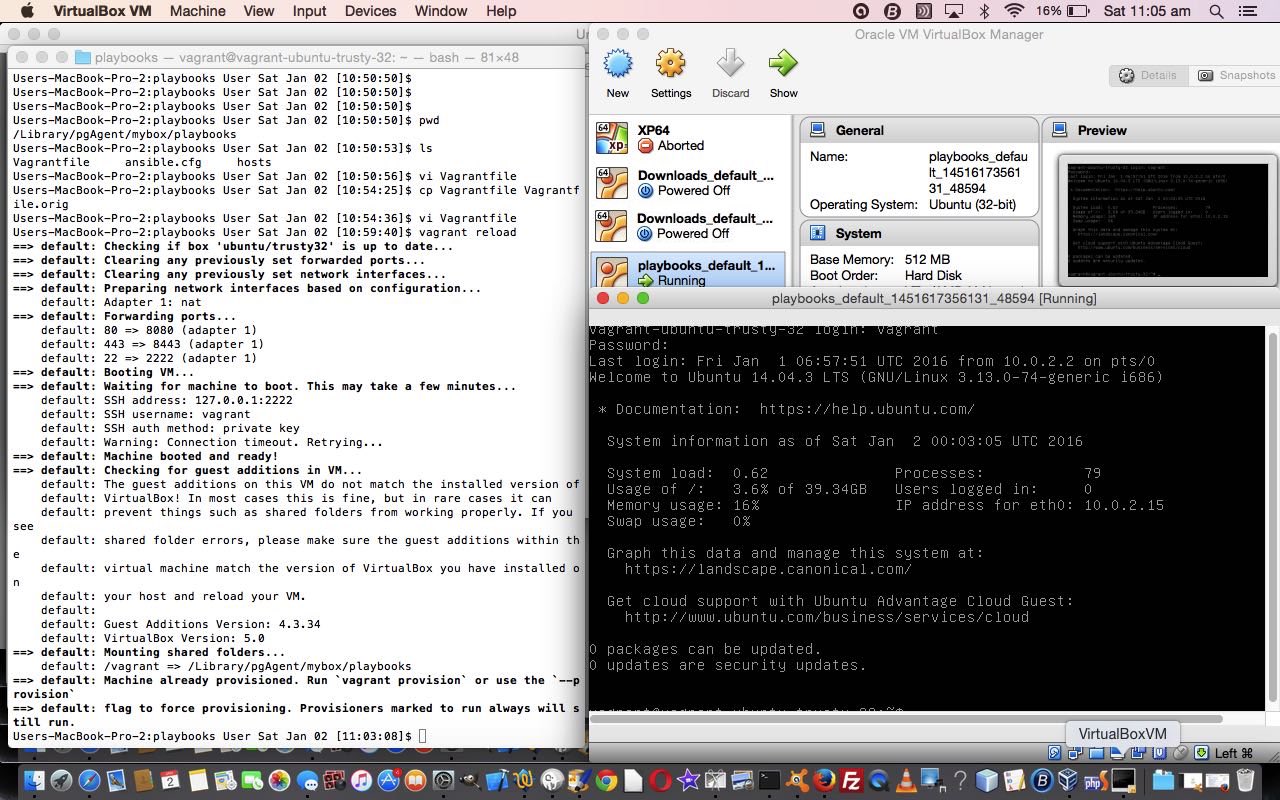 … so now we are going to create a playbook that runs an nginx web server via Ansible playbook (YAML) code (we are going to call web-notls.yml) as below …
… so now we are going to create a playbook that runs an nginx web server via Ansible playbook (YAML) code (we are going to call web-notls.yml) as below …
#!/usr/bin/env ansible-playbook
name: Configure webserver with nginx
hosts: webservers
sudo: True
tasks:
- name: install nginx
apt: name=nginx update_cache=yes
- name: copy nginx config file
copy: src=files/nginx.conf dest=/etc/nginx/sites-available/default
- name: enable configuration
file: >
dest=/etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
src=/etc/nginx/sites-available/default
state=link
- name: copy index.html
template: src=templates/index.html.j2 dest=/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
mode=0644
- name: restart nginx
service: name=nginx state=restarted
… and an nginx configuration file (you could call nginx.conf) …
… and an Ansible template file (you could call index.html.j2) … to result in …
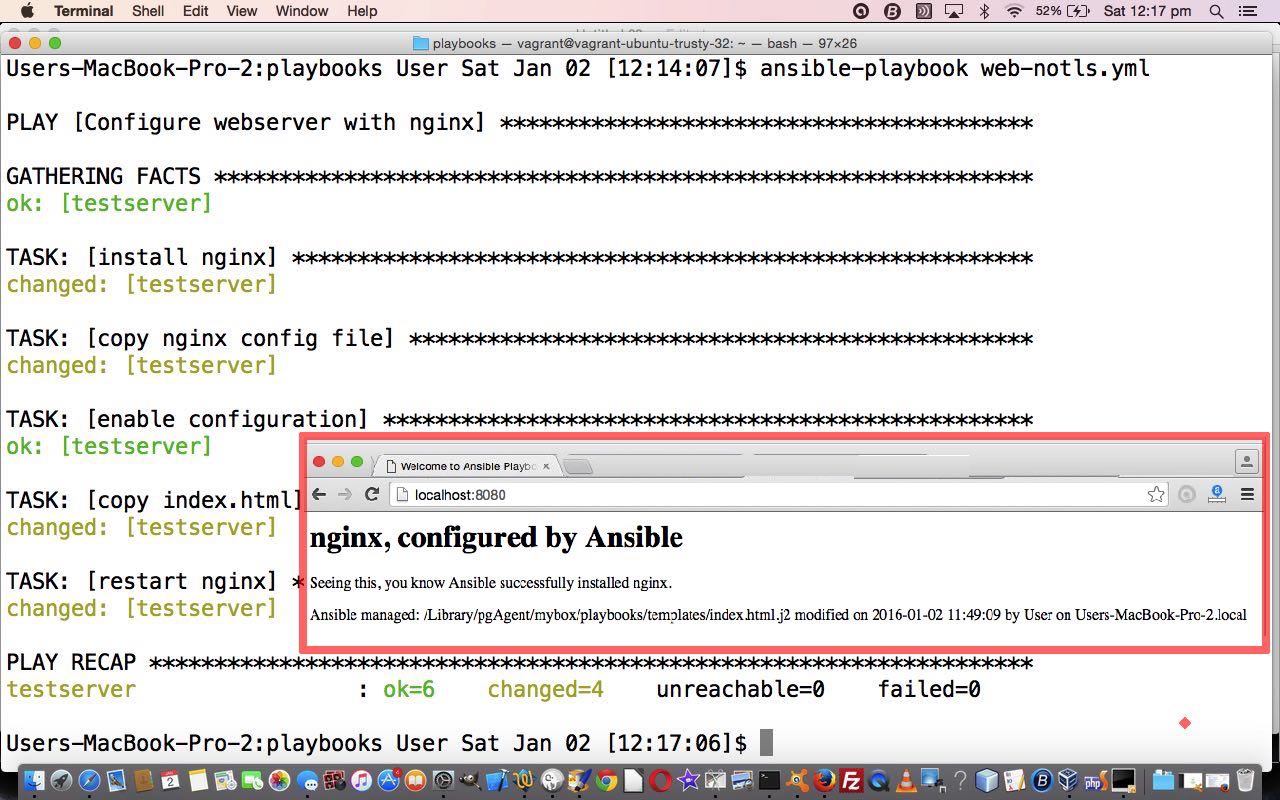
So that’s a simple Ansible playbook example for you, and we hope to develop this further over time. Even so, have to tell you that at the browser going “http://localhost:8080” for a while I was getting ‘Safari can’t open the page “localhost:8080/index.html” because the server unexpectedly dropped the connection. This sometimes occurs when the server is busy. Wait for a few minutes, and then try again.’ As ansible-playbook web-notls.yml had shown no errors, tried ansible-playbook -vvvv web-notls.yml with no difference. After lot of looking around found it to be an “up to” threefold issue …
- misspelling in nginx.conf leaving out the first 6 (in “ipv6only”)
- do System Preferences… -> Sharing show Remote Login is ticked on as per advice of this link?
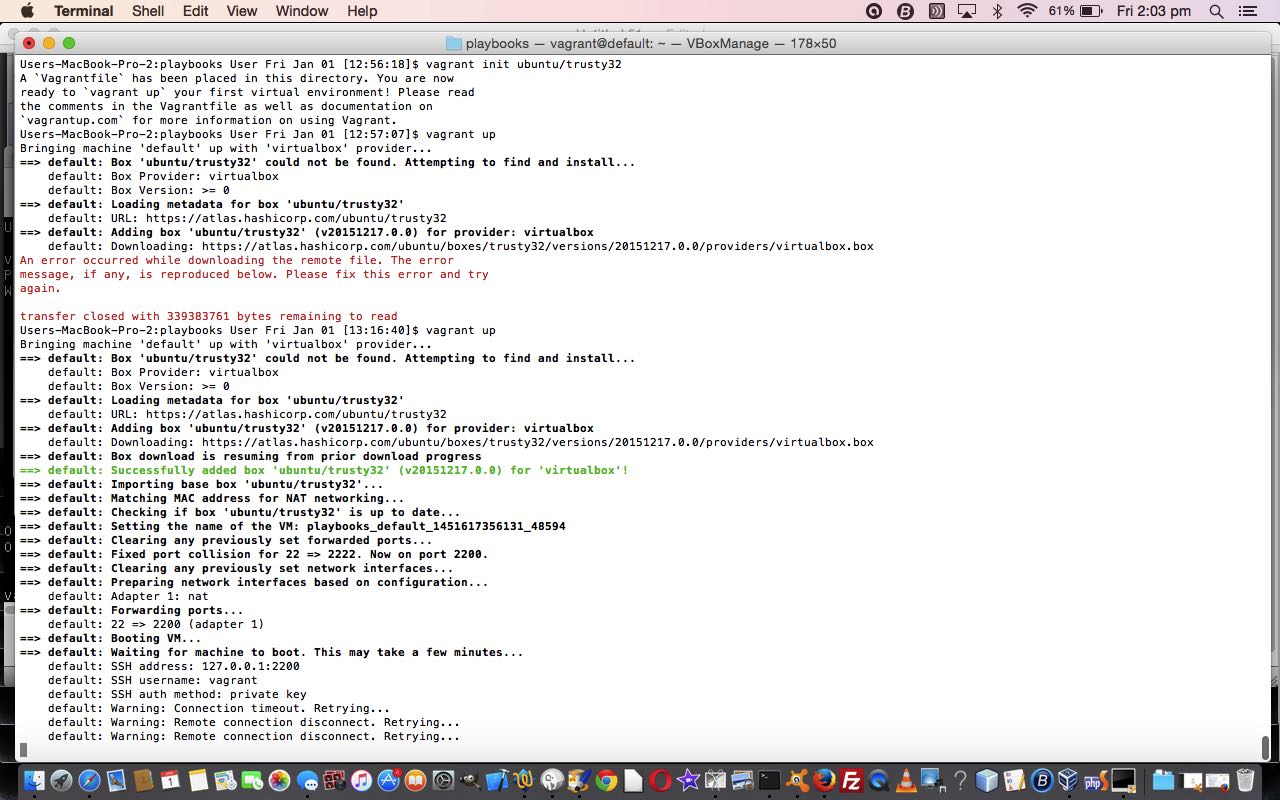
- you may have been an eagle eyed one to notice that 2 days ago we had a (SSH friendly) port of 2200 being used for the “testserver” Ansible server of use (this happened due to some previous Ansible work) but this means that 2 days ago a record was written to ~/.ssh/known_hosts for 127.0.0.1:2200 during that vagrant up run. Now, as today’s work has not caused any initialization vagrant commands, nor even vagrant halt nor vagrant up to occur, when we ran vagrant reload after changing Vagrantfile for those forwarding port changes made the default (SSH friendly) port 2222 come back into play and write a new record for 127.0.0.1:2222 at the end of ~/.ssh/known_hosts (and how was this lead gotten to? … the “ssh -i .vagrant/machines/default/virtualbox/private_key vagrant@127.0.0.1 -p 2200” of 2 days ago was rerun today as “ssh -i .vagrant/machines/default/virtualbox/private_key vagrant@127.0.0.1 -p 2222” and caused an SSH error …
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
@ WARNING: REMOTE HOST IDENTIFICATION HAS CHANGED! @
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
IT IS POSSIBLE THAT SOMEONE IS DOING SOMETHING NASTY!
Someone could be eavesdropping on you right now (man-in-the-middle attack)!
It is also possible that a host key has just been changed.
The fingerprint for the RSA key sent by the remote host is
87:blah:blah:blah:57.
Please contact your system administrator.
Add correct host key in /Library/pgAgent/.ssh/known_hosts to get rid of this message.
Offending RSA key in /Library/pgAgent/.ssh/known_hosts:8
RSA host key for [127.0.0.1]:2222 has changed and you have requested strict checking.
Host key verification failed.
). Now those two records at the end of ~/.ssh/known_hosts were different. Making them the same except for the port number (doh!) made things work for the nginx server at http://localhost:8080/ … so might an initialization vagrant scenario (plus all the rest), but didn’t try that.
Previous relevant Vagrant Primer Tutorial is shown below.
In understanding what is out there on the net, tend to want to form relationships in my mind, between applications.
So here’s a good one … VirtualBox with Vagrant … or perhaps … VirtualMachine with Vagrant.
So here’s another one that’ll knock your socks off (and you’ll want to read after/before/same time/while having corn flakes as today (to get it all in context, if this is new knowledge)) … Ansible with Vagrant, that we talked about yesterday with Ansible Hello World Primer Tutorial as shown below. As you read it, take note of the title of the book we recommend … “Ansible Up and Running” by Lorin Hochstein … the word “up” is bound to be in the list of a deployer’s favourite words, and is critical to all “Vagrant” talk as its favourite command (and its “nirvana” (if successful), and is slow the first time (when “vagrant up” is often preceded by an initialization vagrant command such as “vagrant init ubuntu/trusty32”) with a project on an individual programmer’s system, but fast from then on for that programmer “revisiting”, so that on multiple projects they’re zooming (ie. cd’ing) around to places and going “vagrant up” vagrant up vagrant up vagrant up) is …
vagrant up
… and for today’s book recommendation … “Vagrant Up and Running” by Mitchell Hashimoto … fancy that?!
So what’s Vagrant? And why is it so friendly?
Can try to answer the first now, but the second one relates to early times spent with Caspar the Ghost … but we digress.
To quote the Vagrant landing page …
Create and configure lightweight, reproducible, and portable development environments.
What we understand in layperson’s terms is that if a client plonks a “system” on your doorstep and says any of …
- “Fix this.”
- “Maintain this.”
- “Make it do this, now (awwwwwwwright … after lunch, then).”
… Vagrant may interface to an IDE like PHPStorm (which we’ll talk about soon) or use Git (or GitHub) and/or Composer in a Work Flow helping a group of team leaders and dbas and analysts and programmers achieve this by …
- simulating the whole system
- modelling the whole system
- changing and modifying the resultant model, to check things improve, and still work, hopefully
- deploy this model back onto the reality, for the client to model a broad grin, hopefully
Without this Vagrant and VirtualDisk (or VMWare) relationship, the job can be done, but you often find the (different) environment (between the programmer environments and the client environment) causes problems during the deployment phase, whereas using these products helps mitigate against these issues. Comprehendo?
Previous relevant Ansible Hello World Primer Tutorial is shown below.
The role of a programmer is expanding into deployment with software tools such as Ansible, because it has the capability of making the piloting of automation systems “approachable” as an “art”.
Why would you want to “pilot an automation system”? Well, to see the whole picture, when you (are part of a team that) are given a software project of improving a “system”, wouldn’t it be great to …
- model that customer system at a snapshot of time
- be able to work and test on that model away from the customer environment until satisfaction
- after changes are tested to satisfaction, redeploy to the customer’s live system via software changes made to the model, and perhaps to data and configuration settings as well
? We think it sounds very good, especially with Ansible helping out with that modelling, because a lot of the doubt in a programmer’s head when working away from a customer site’s environment (back at their office, perhaps) on a project that is going to be deployed back at the customer is that what they are seeing working, may not work when taken back and deployed onto the customer site’s environment again. The work methods above help to mitigate that, and Ansible really helps with the deployment aspects to the whole job, leaving programmers more time to get back to what they enjoy the most, methinks … programming and unit testing.
Without Ansible, achieving a project with new (never before used) software tools required, involves programmers working out the configuration management aspects to the job via Search Engine Searches (with a lot of “Adding to Favourites”) and/or the recalling of online documents (often from the OpenSource world), and trialling configurations, hopefully combined with personalized accompanying documentation. Employing Ansible into the planning may still involve this initial effort, but should never happen again, because what you are left with will be an Ansible approach capturing knowledge that has a far better chance of staying up to date.
Ansible is pretty obviously most advantageous in complex deployment scenarios, but it can be applied to the one server (and we are talking Linux or Unix with this today, but Windows is also supported) scenario as well, and we’ll be showing a bit of this today, to show you a bit about how Ansible works.
Let’s, before that, do a glossary list of terms (mainly from Wikipedia .. thanks) we might use in relation to Ansible …
- configuration management … that’s Ansible
- provisioning tool … that’s Ansible
- Ansible on GitHub by Michael DeHaan
- SSH
- YAML (and Playbooks)
- JSON
- package manager … eg. Homebrew, apt, YUM, MacPorts, pip, RPM, OpenPKG, nix, Conary, dpkg, Cygwin
- Jinja (Python) template engine
- development stack
- deployment
- virtual machine
- automation
- source control
- VirtualBox
- Vagrant … more tomorrow here
- GitHub
- PHPStorm IDE we’ve mentioned before here (integrates some of concepts above)
… and direct you towards a good book, namely “Ansible Up and Running” by Lorin Hochstein, from which a lot of today’s blog posting’s information is derived … so, thanks.
Okay, so what will we do with Ansible?
Install Ansible … on Mac OS X (via Terminal application) … and you’ll need ssh (if “ssh” on command line means nothing) … if you have Homebrew package manager installed you can go …
… or you can install as root via Python’s pip package manager …
$ sudo pip install ansible
… or another way to install as root via the apt package manager …
$ sudo apt-add-repository -y ppa:ansible/ansible
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install -y ansible
… or you can install into a Python (2.6 or above) virtualenv with wget via …
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mitsuhiko/pipsi/master/get-pipsi.py
$ python get-pipsi.py
$ pipsi install ansible
( with an updating of PATH to include ~/.local/bin ) … or you can use GitHub via …
$ git clone https://github.com/ansible/ansible.git --recursive
… so that you can have …
$ ansible
… mean something at a command prompt (if not, a “find / -name ‘ansible’ 2> /dev/null” and adjustment of PATH in ~/.profile may be necessary) … a suffix of ” -vvvv” is useful for debugging purposes.
Show you a 127.0.0.1 local web server with VirtualBox “Hello World” feeling example using Ansible involved the need for installation, as required of Oracle’s VirtualBox and, for tomorrow specifically, we talk about Vagrant via …
… then, working off the install we made of Ansible we found an example hosts file off the install, and copied it to /etc/ansible/hosts.orig as shown by …
$ cd $HOME
$ mkdir mybox
$ cd mybox
$ mkdir playbooks
$ cd playbooks
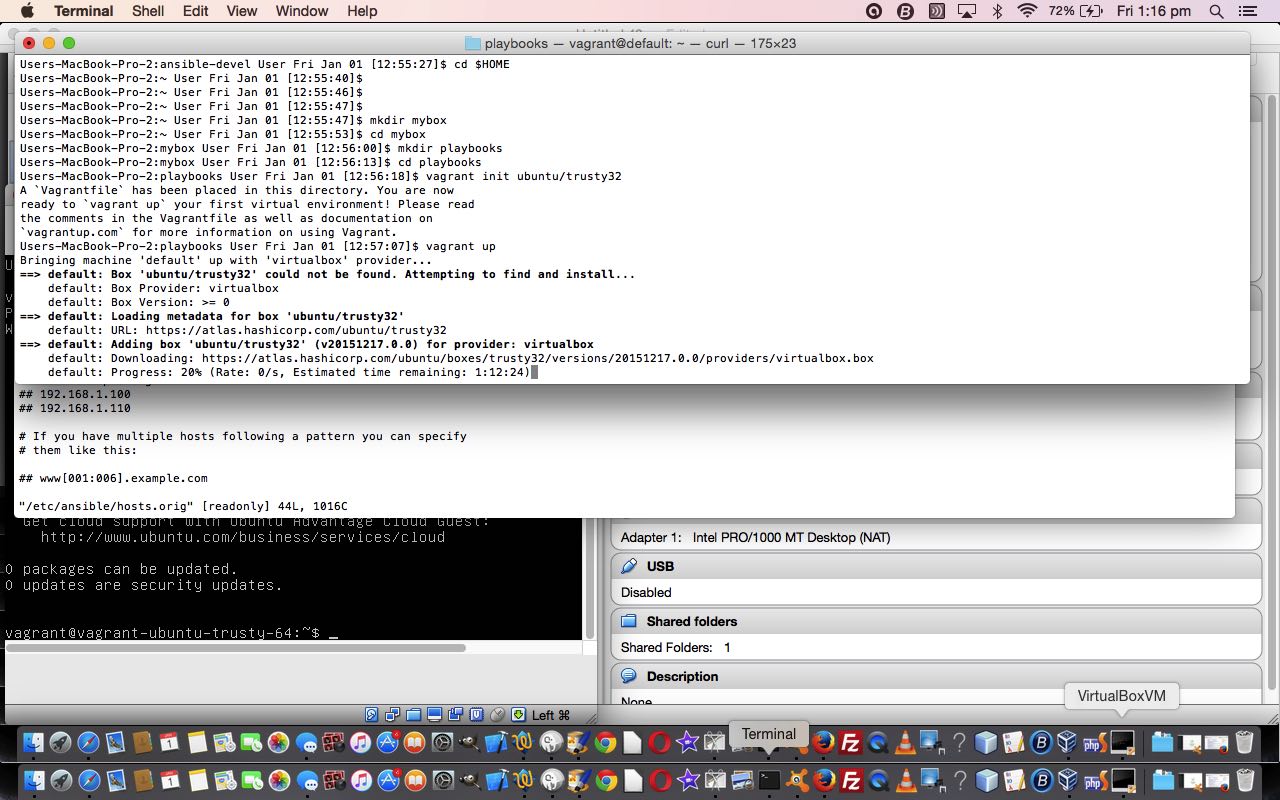
$ vagrant init ubuntu/trusty32
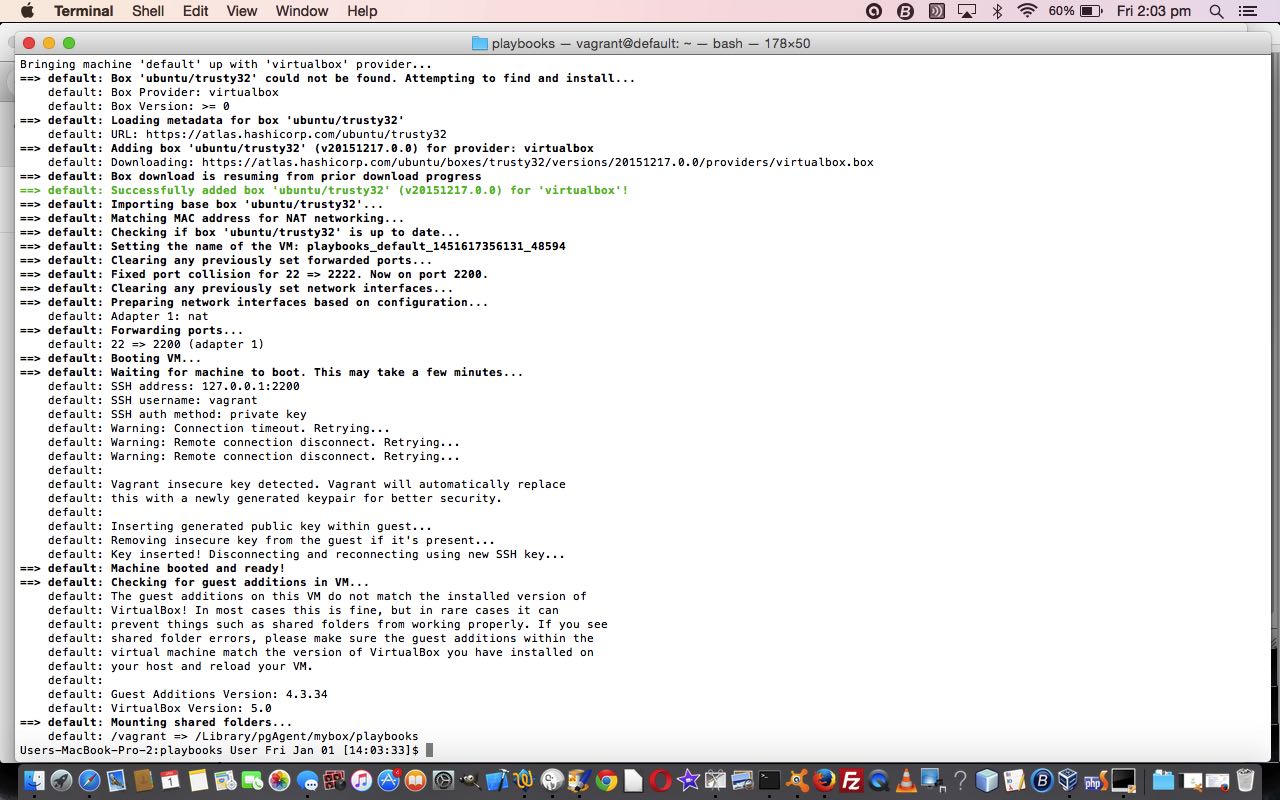
$ vagrant up
$ ssh -i .vagrant/machines/default/virtualbox/private_key vagrant@127.0.0.1 -p 2200
vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-32:~$ echo "Hello World ... via Ansible"
Hello World ... via Ansible
vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-32:~$ exit
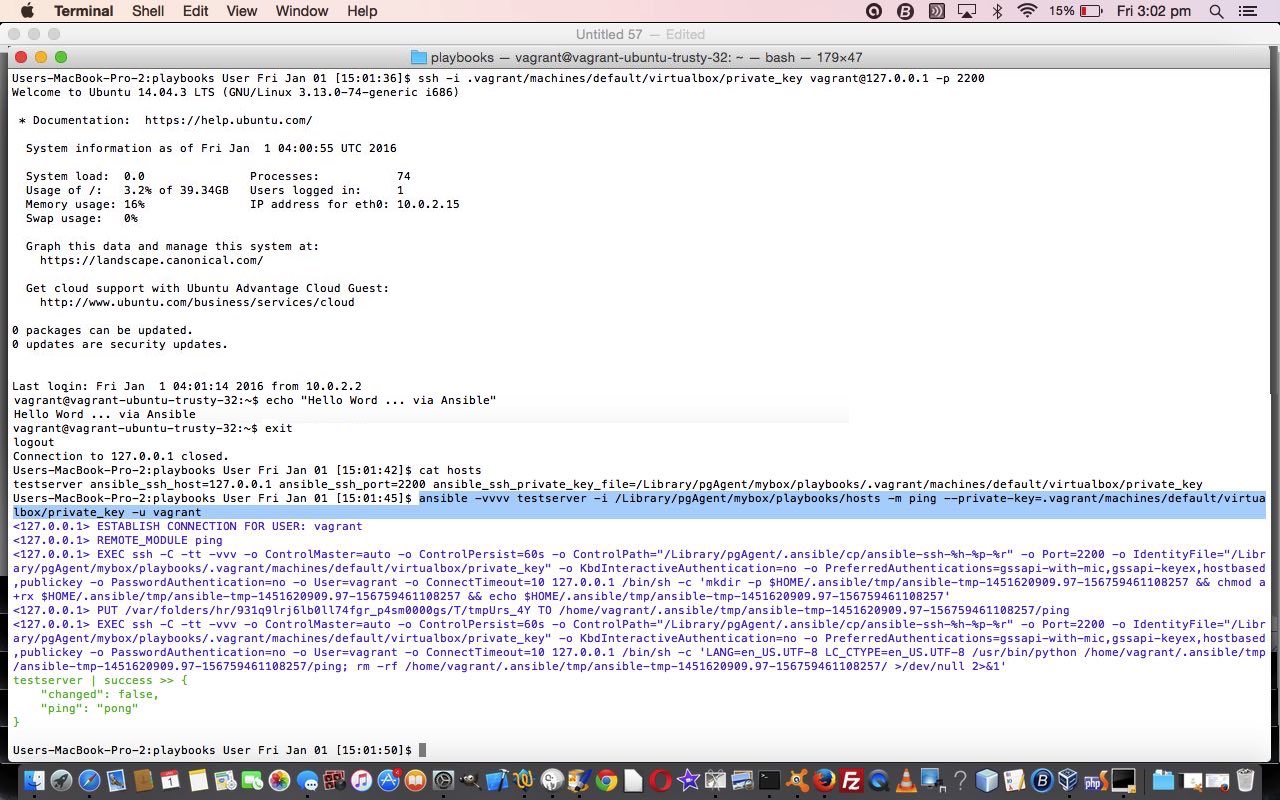
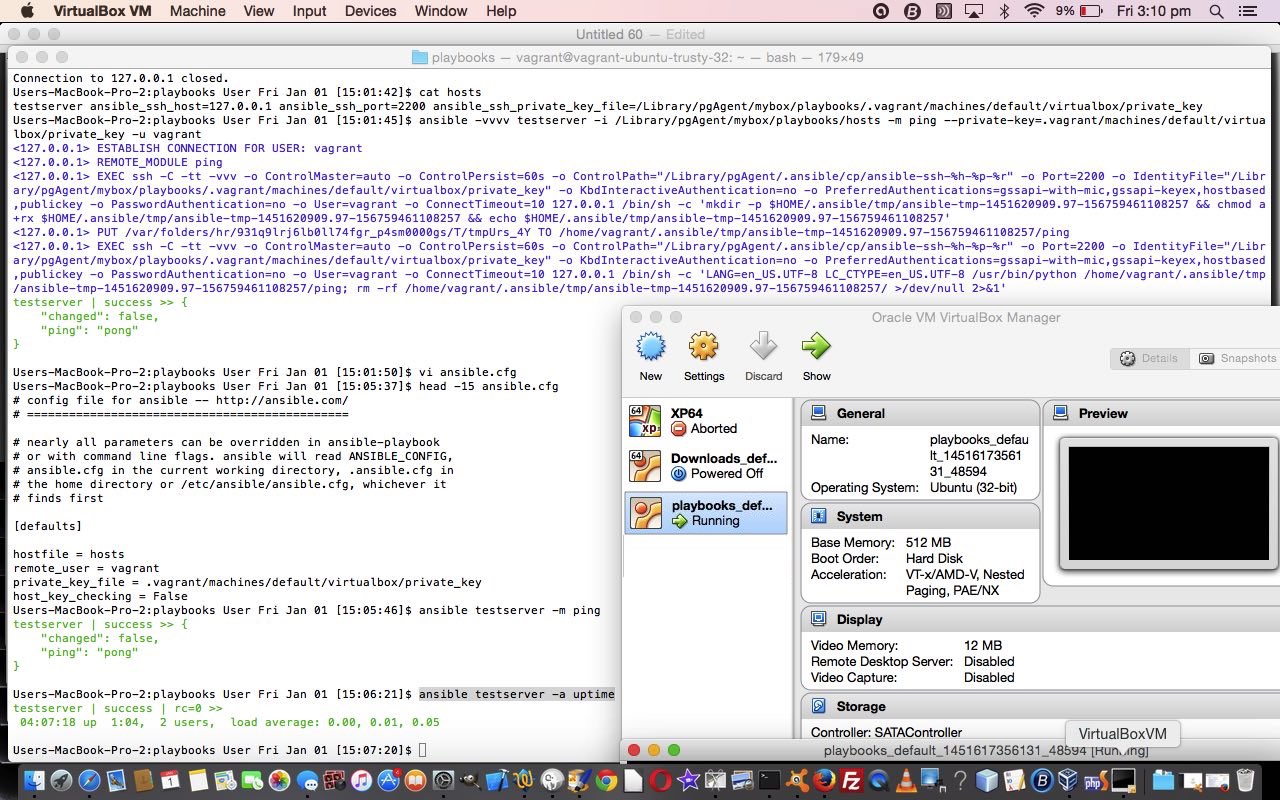
$ cat hosts
$ head -15 ansible.cfg
$ ansible testserver -m ping
$ ansible testserver -a uptime
Ansible is not alone with what it sets out to achieve … think Chef, Puppet or Salt … read more thanks to this useful link for that information.
We hope to be back with more about this powerful product as time goes by. In the meantime, research into Ansible Playbooks would be a great idea.
If this was interesting you may be interested in this too.
If this was interesting you may be interested in this too.
If this was interesting you may be interested in this too.



10 Responses to Ansible Playbook Primer Tutorial