Yesterday’s web application game “Subject Areas” of HTML/Javascript Subject Areas Game Data Attributes Tutorial, as shown below, came in very handy as the starting point for the design and a large part of the workflow and coding of today’s “Comparisons and Superlatives” game, again primarily designed for testing and/or improving some question sentence construction skills for ESL (or “English as a Second or Foreign Language”) students. It’s easy to ask the questions, but getting the computer to answer … Gooooooooooogggggggglllllllleeeee?!
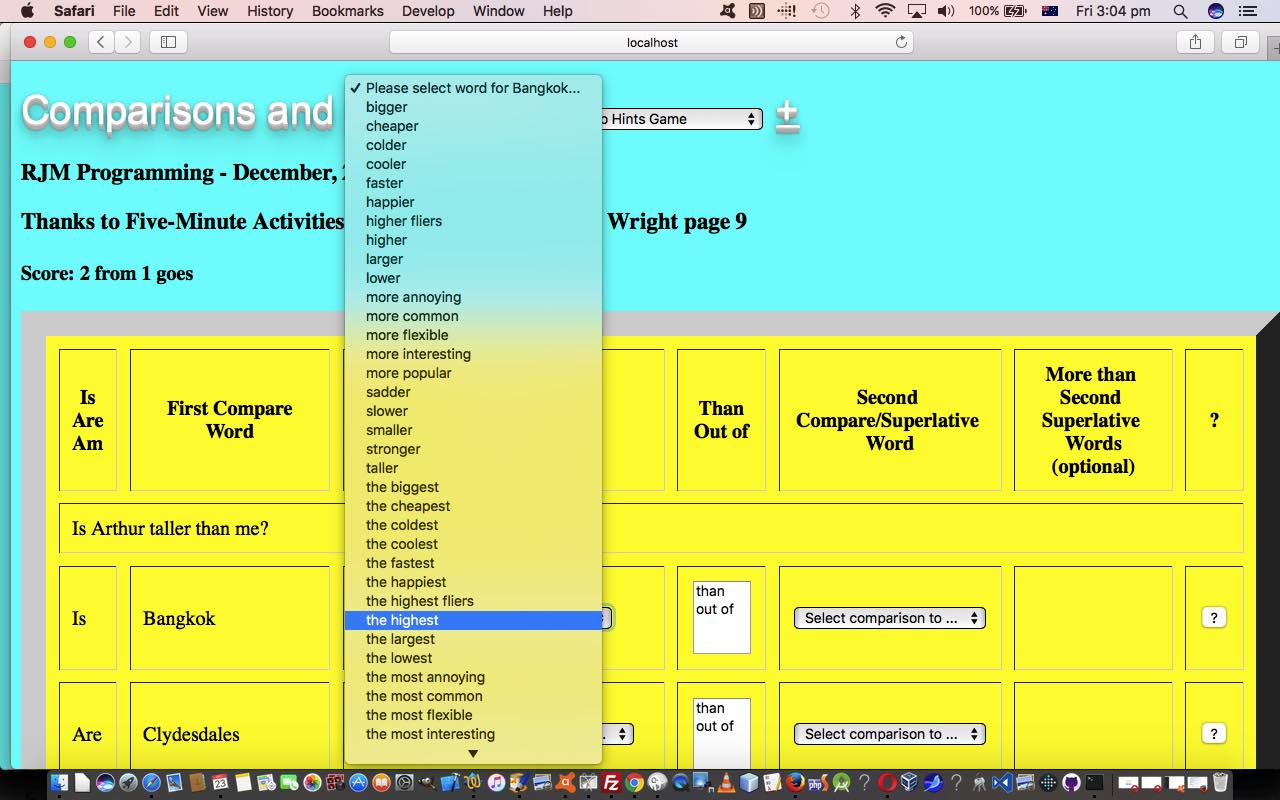
So it’s big … bigger … biggest types of thinking with the game today, where the subject word(s) (where the rest of the (question) sentence (we were taught at school, in English grammar, is the predicate)) is matched by the user, interactively, with a suitable …
- comparative adjective … eg. taller … or …
- superlative adjective … eg. (the) tallest
… along with a loose sanity check on sense, and then the user proceeds to also define a suitable …
- comparison object word(s) … and optionally …
- (additional) superlative object word(s) (prefixed by ” and “)
In doing this, and seeing the (question) sentences work, or not, you see that it is an “object” at play here, because where we have “subject” pronouns in the left hand list, by the time we want them to work in the right hand dropdown list of potential “object” pronouns we had to change their form, to have the (question) sentences be well formed sentences. An example here is the “she” (as a subject) on the left hand column becomes “her” (as an object) on the right hand dropdown list. This happens less with “subject” nouns.
So why not try our live run or peruse the HTML and Javascript code behind its operation with compared_to.htm today?
Before we go, a catch up on thank yous to Five-Minute Activities by Penny Ur and Andrew Wright … ISBN: 978-0-521-39781-0 …
- Page 9 for today’s Superlative Comparing game … and …
- Page 54 for inspiration for yesterday’s Subject Areas game
Previous relevant HTML/Javascript Subject Areas Game Data Attributes Tutorial is shown below.
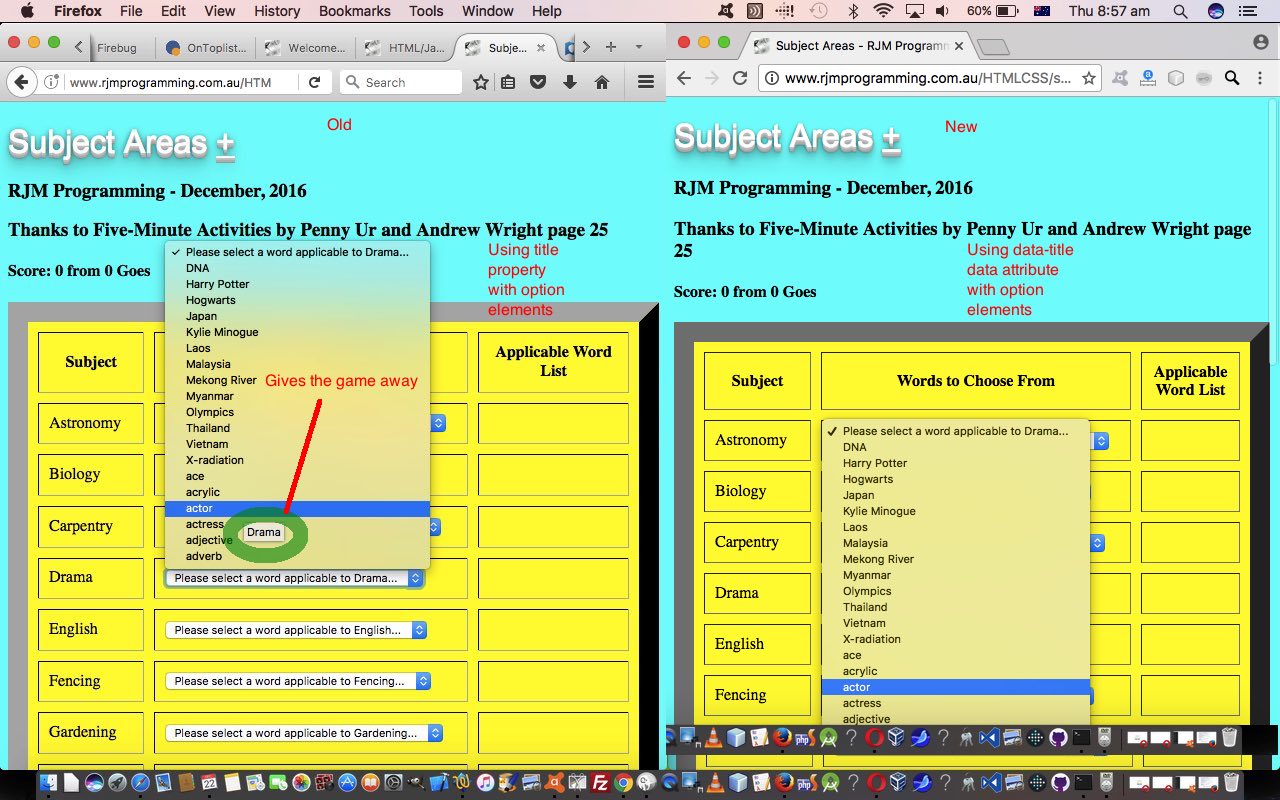
Yesterday’s web application game “Subject Areas” which we started with HTML/Javascript Subject Areas Game Tutorial had a weakness in “UX” terms, and only for non-mobile platforms where onmouseover event means something … but a weakness nonetheless. Perhaps it is good to develop a sense of such issues annoying you, and that way you learn things.
So what are the specifics of this “weakness” (for non-mobile users)? The dropdown being hovered on, in the old ways of yesterday, can give the game away, and make it too easy for the user to get the answer with no “thinking” effort. The reason this has happened is due to the “old way” of adding a title property to all of the HTML option elements, that we use in a true data sense to make our game work … but nonetheless is the “weakness” we can remedy … with … data attributes and we’ve talked about this before at XML to HTML PHP Three Ways Translation Tutorial. And don’t want to come over all school masterish ‘n all, but … and isn’t there always a butt … but this is an important aspect to adding data intelligence to your HTML work, and it doesn’t surprise me that in the title of that time we talked about it before there is “XML” mentioned. XML normally has a lot of data intelligence, but data attributes can help you get towards some of that with your HTML web application work. Specifically, HTML/Javascript code-wise … we …
- used to, with HTML option elements, using the title property …
- define via …
selinnards += "<option title='" + ourwordlist[i].split(';')[1] + "' value='" + ourwordlist[i].split(';')[0] + "'>" + ourwordlist[i].split(';')[0] + "</option>";
- reference via …
if ((',' + selo.options[selo.selectedIndex].title + ',').indexOf((',' + versus + ',')) != -1) {
// more code here
}
- define via …
- … versus … we now, with HTML option elements, using the data attribute “homespun” data-title data attribute …
- define via …
selinnards += "<option data-title='" + ourwordlist[i].split(';')[1] + "' value='" + ourwordlist[i].split(';')[0] + "'>" + ourwordlist[i].split(';')[0] + "</option>";
- reference via …
if ((',' + selo.options[selo.selectedIndex].getAttribute('data-title') + ',').indexOf((',' + versus + ',')) != -1) {
// more code here
}
- define via …
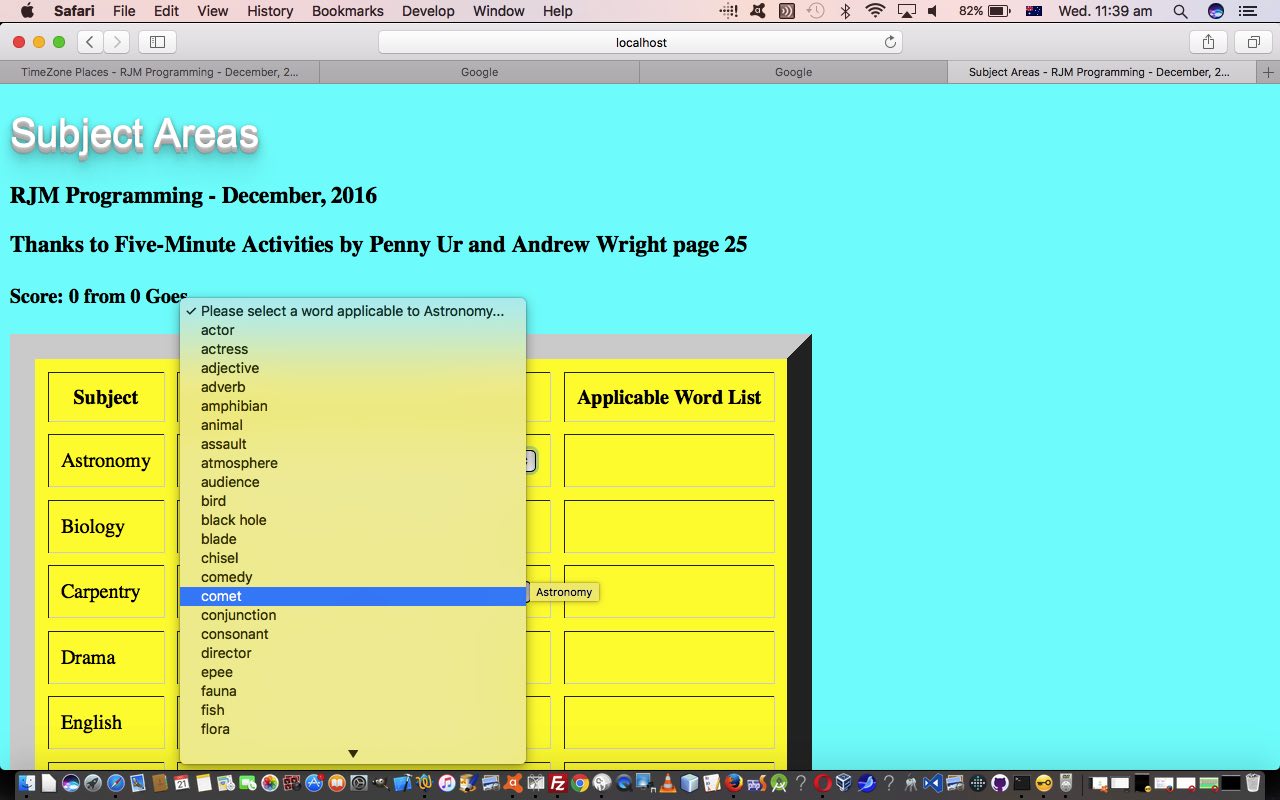
Try our live run (and/or compare it to the old ways live run) or peruse the HTML and Javascript code behind its operation with subject_areas.html today, changed from yesterday in this way. Now you may notice examining this code, it does not exactly look as above, but this code above was working (and would still work) after an epiphany we had … but please don’t spread this epiphany around … especially on dry rye bread … that non-mobile users can have an improved game working this idea above, because there are probably ESL students, or others, who may want the hints that the onmouseover title property usage give, so how about we add a degree of difficulty concept to the game, for them, via …
- as new global variables …
var mode='difficult';
var modeprefix='data-';
- at onload event (unchanged code) but changed HTML just below that …
<body onload=" fillintable(0,''); " style="background-color:aqua;">
<h1>Subject Areas <div id='ifnm' style=display:inline;></div> <a title='Your Own Subject Area' style='text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;' onclick='ask();'>+</a></h1>
- and at fillintable(0,”) call of function, the new code …
function locy(thisvalue) {
location.href='./subject_areas.htm?score=' + score + '&goes=' + goes + '&difficulty=' + thisvalue;
}
function fillintable(phase,addthis) {
var i,j,thisrow="",thesewords,k,selinnards='';
if (phase == 0) {
mode=location.search.split('difficulty=')[1] ? location.search.split('difficulty=')[1].split('&')[0] : 'difficult';
if (navigator.userAgent.match(/Android|BlackBerry|iPhone|iPad|iPod|Opera Mini|IEMobile/i)) {
phase=phase;
} else if (mode.replace('difficult','') != '') {
modeprefix='';
document.getElementById('ifnm').innerHTML='<select onchange=" locy(this.value); "><option value=easy>Hints (on hover) Game</option><option value=difficult>No Hints Game</option></select>';
} else {
document.getElementById('ifnm').innerHTML='<select onchange=" locy(this.value); "><option value=difficult>No Hints Game</option><option value=easy>Hints (on hover) Game</option></select>';
}
var addit=location.search.split('addthis=')[1] ? decodeURIComponent(location.search.split('addthis=')[1]).split('&')[0] : '';
- and at the define, the code ideas coalesce, via …
selinnards += "<option " + modeprefix + "title='" + ourwordlist[i].split(';')[1] + "' value='" + ourwordlist[i].split(';')[0] + "'>" + ourwordlist[i].split(';')[0] + "</option>";
- and at the reference, the code ideas coalesce, via …
if ((',' + selo.options[selo.selectedIndex].getAttribute(modeprefix + 'title') + ',').indexOf((',' + versus + ',')) != -1) {
// more code here
}
As you can see, we really like Javascript global variables, but if you are like us in this way, be aware that this is not such a popular opinion.
Previous relevant HTML/Javascript Subject Areas Game Tutorial is shown below.
We’ve called today’s web application game “Subject Areas”, primarily designed for testing and/or improving the vocabulary skills for ESL (or “English as a Second or Foreign Language”) students.
We humans love to categorize things, and today, with this game of ours, we are facilitating that penchant we have by our “categories” being “Subjects”, like at school or in life, and the user of the game is asked to look down a list of words to pick ones where the word has a synergy with the “Subject”. They score a point if we agree, and don’t think we don’t know if you cheat?!!?!?
So why not try our live run (which, today, acts differently to the web application that happens when you click the tutorial picture … more on that tomorrow, if you can’t guess it yourself?!) or peruse the HTML and Javascript code behind its operation with subject_areas.html today (or at WordPress 4.1.1’s HTML/Javascript Subject Areas Game Tutorial)? That wasn’t rhetorical, was it?!
If this was interesting you may be interested in this too.
If this was interesting you may be interested in this too.
If this was interesting you may be interested in this too.