We’re starting down the road of PHP mcrypt encryption and decryption methods for a Membership Website, today establishing three webpages (that might be all you need to know … we’ll see) …
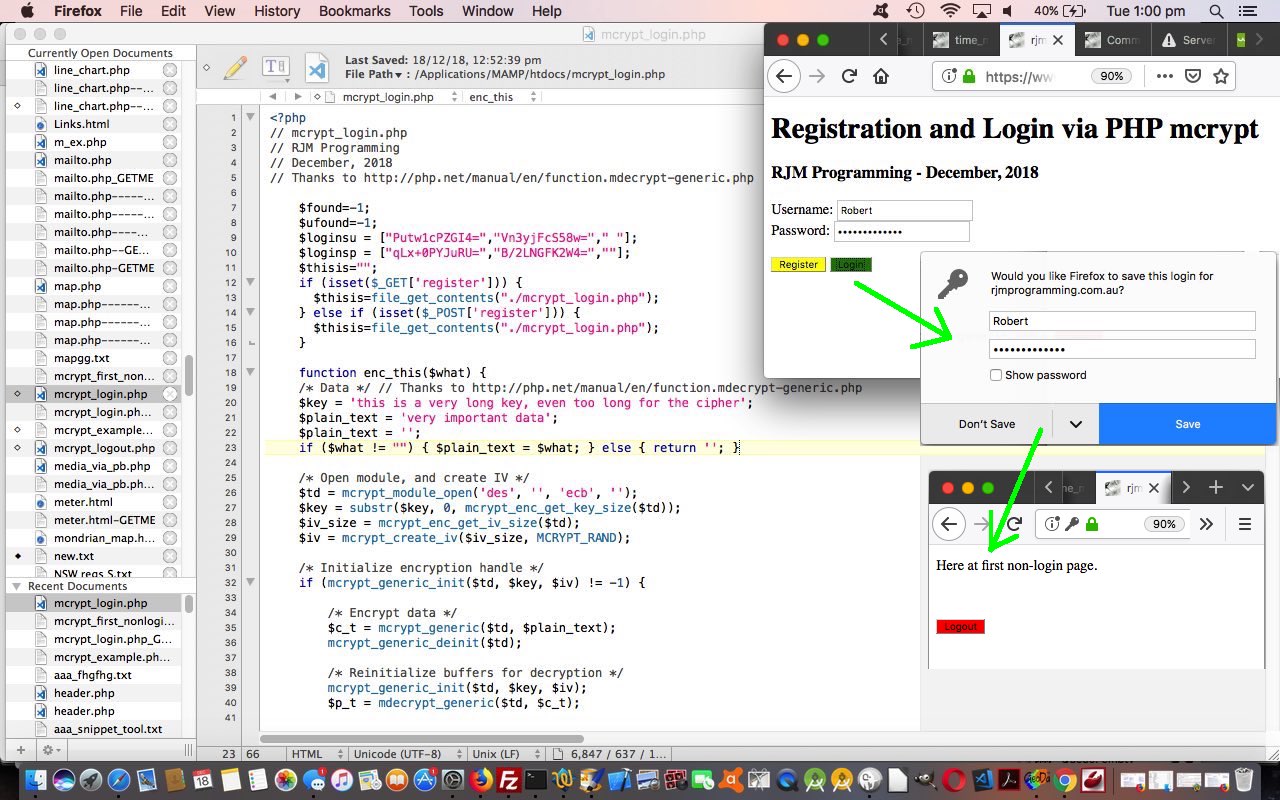
- mcrypt_login.php webpage handles “Register” and “Login” (button functionalities) … and that, if successful will navigate the user to …
- mcrypt_first_nonlogin.php webpage can be your template …
<?php
// mcrypt_first_nonlogin.php
// RJM Programming
// December, 2018
// Thanks to http://php.net/manual/en/function.mdecrypt-generic.php
session_start();
if ($_SESSION['username']) {
echo "<!doctype html><html><head><title>Registration and Login via PHP Mcrypt - RJM Programming - December, 2018</title></head><body><p>Here at first non-login page.</p><br><br><input onclick=\" location.href='./mcrypt_logout.php'; \" type=button style=background-color:red; value=Logout></input></body></html>";
} else {
echo "<!doctype html><html><head><title>Registration and Login via PHP Mcrypt - RJM Programming - December, 2018</title></head><body onload=\" location.href='./mcrypt_login.php?redirectto=' + encodeURIComponent(document.URL); \"></body></html>";
}
?>
… for any non-login page, that offers a “Logout” button … that calls … - mcrypt_logout.php webpage to clear the $_SESSION[] of the successful Login session, ready for another, as the user requires
Don’t we need to mention a database or cookies or localStorage here? Well, not really, because we self-contain the login data into the inaccessible (to the outside world) PHP code itself, getting the PHP to update itself on a successful click of the “Register” button. That PHP updating of itself uses …
… in amongst its avoidance of showing any real username or password anywhere, even if that “anywhere” place is inaccessible to the world anyway. In these terms why don’t you try out mcrypt_login.php‘s live run to see what we mean (and if you do not feel like adding your own Registration you can use “Robert” and “testing_times” as a Login here). As you examine the PHP codesets above, see how $_SESSION[‘username’] usage stops a user coming into mcrypt_first_nonlogin.php (and try that for yourself here if you like) without logging in.
Then, perhaps, compare and contrast to previous (PHP) Registration thinking in Registration via Captcha Primer Tutorial below.
Previous relevant Registration via Captcha Primer Tutorial is shown below.
We, pretty obviously, spoke too soon, yesterday, that that was it, or words to that effect, with this topic, and that is no wonder, as it covers a lot of territory.
Up to now, we’ve restricted its scope, hugely, by saying there are only “admin” users and “guest” users involved with …
… the idea that the “Things That We Have in Common” far outweigh the things that divide us, and present some ideas here …
… because with a real blog or CMS or social media scenario there are real users with real needs that it is preferable to cater for with real software … so even though we are still just theoretical here, short of a full blown website, let’s get onto the topic of “registration”. “Registration” is the creation of a new user registered with your web application, that you see a lot of, all over the web.
Ideally you register a real human user, though we would really enjoy any Martian to register (for free, plus a prize of one free Earth Bar) … but we digress. So today we channel the tutorial of yesterday to go over the top with CAPTCHA again. In fairness to CAPTCHA, though, the best place to use it is during login and/or registration procedures.
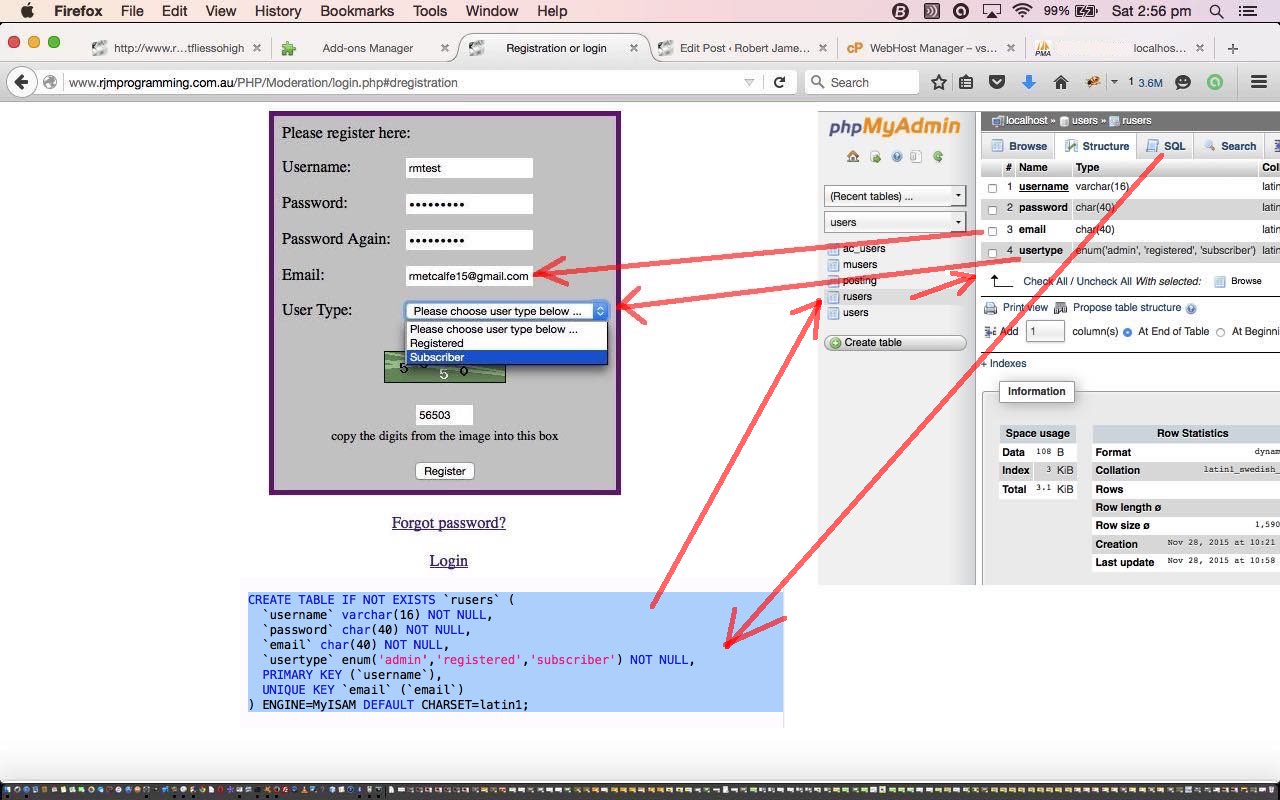
What are the changes that phpMyAdmin helps us with regarding the database … well, with regard to the `rusers` MySql table we have we append to the pre-existing …
- username
- password … columns, the new …
- usertype
… because, respectively, `email` is great to use both for what it is, and as a database uniqueness constraint method, and `usertype` is where we define our new list of user types, namely …
- admin … the only real type up to now … but, as of today, specifiable (in addition to “guest” users) are …
- registered
- subscriber
… and ask the user what they want to be out of those last two. We don’t do so much different here, but we just want to show you today an approach to organize yourself regarding compartmentalizing this “real world” real user thinking that is a bit like “shelling peas” once all this is set up … and modularizable and job-assignment-to-a-worker-friendly because you get to a one PHP set of code per one user type scenario, once you’re finished.
As you might imagine the biggest changes today are to our login.php rather than to member.php and moderator_captcha.php (the main changers yesterday) …
Here is the login PHP code for all registered users you could call login.php with its admin user useful live run, changed a lot from previously to handle registration and more varied user types this way.
Here is the member PHP code that follows the login(.php) page you could call member.php changed a little (but very importantly) from yesterday’s work this way to restrict its usage to ‘admin’ user types.
Here is new template like PHP code (nirvana for PHP Membership Website Primer Tutorial) for registered users you could call registered.php
Here is new template like PHP code (nirvana for PHP Membership Website Primer Tutorial) for subscriber users you could call subscriber.php
We found two great book sources researching these blog posts, particularly regarding the subject of “membership”. They are …
- PHP and MySql Web Development by Luke Welling, Laura Thomson
- Professional PHP Programming by Jesus Castagnetto, Haeish Rawat, Sascha Schumann, Chris Scollo, Deepak Veliath … chapter 20
Finally, here is a live run link that interfaces this to the moderation ideas of previous days.
Previous relevant Moderation by Captcha Primer Tutorial is shown below.
In our “onions of the 4th dimension” world we have an onion layer of thought today regarding “moderation”.
Let me just quietly ask? Are you a robot? Mr Turing posed this very fundamental question some time back. But the fact is, a lot of visitors to just about everybody’s website are robots (shock! … horror!), else how else would Search Engines get updated information, but to “crawl” your website (as I say this, forgot to say how blogs like WordPress ping Search Engines), man person.
And just to get in (really) early (with the way modern technology is shaping) … “Not that there’s anything wrong with being a robot” (if only Seinfeld had watched Humans … Jerry?! George?!).
So let’s talk about CAPTCHA, which we have not capitalized in the blog title, because we hate shouting too much here. It is a way to try to verify the web application is dealing with a real human being, as we intimated above. As such, you may want to consider it a replacement for “moderation”, but this is not advisable, because, alas, not all the nasty stuff on the net can be attributed to robots … far from it. But it is a good idea up to a point. My personal objection to its use revolves around the disturbance of usage for some disabled users, though am sure there are really sophisticated CAPTCHA plugins for all the scenarios out there.
Today’s work places a CAPTCHA layer on top of all four previously talked about modes of “moderation”, as per …
- no moderation … even this needs a server side language, in our eyes, because you will be changing a server side webpage for all users
- email (or sms or voicemail or any direct communication method) moderation … ask for an admin user of the website to change things after having emailed them … this is the one we showed three days back … and please feel free to try your own entries
- moderate via a (web server) database with posting statuses such as “Awaiting Moderation”, “Published”, “To Be Deleted” … this is the one we showed yesterday … and, yet again, please feel free to try your own entries
- moderate via a system of (web server) files with posting statuses such as “Awaiting Moderation”, “Published”, “To Be Deleted” … this is the one we showed two days back … and, again, please feel free to try your own entries
- only moderate to either of the four above after having gone through a CAPTCHA test that the user is not a robot … this is the one we show today
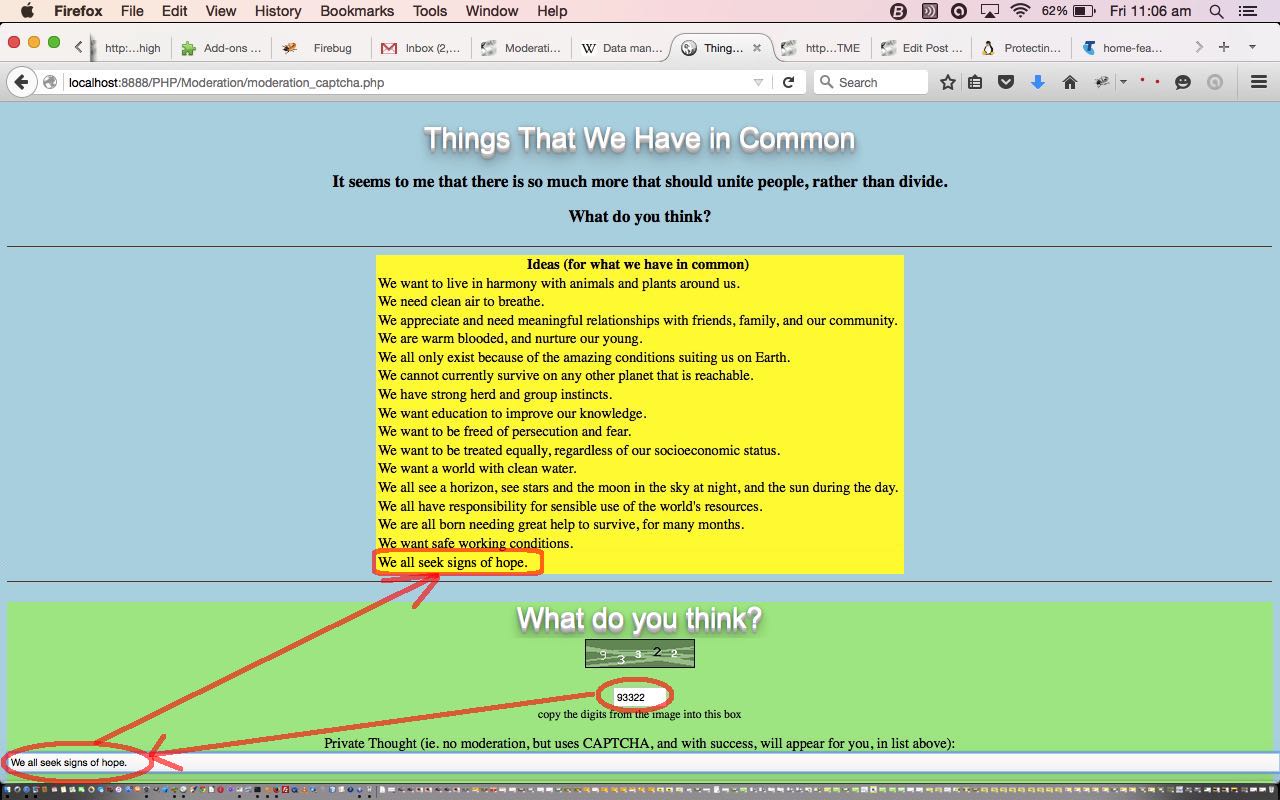
To get the PHP CAPTCHA functionality going we thank this very useful link from “The Art of Web” website. Its precise and clever advice creates the imagery required to present a CAPTCHA image to the user that contains five digits for the user to enter to verify to the web application that they are human. The web application CAPTCHA logic is applied to all the method=POST forms used (and a new form was encased around the “private moderation” (ie. no moderation) case) via the HTML form’s …
... onsubmit="return checkForm(this);" ...
… validation method.
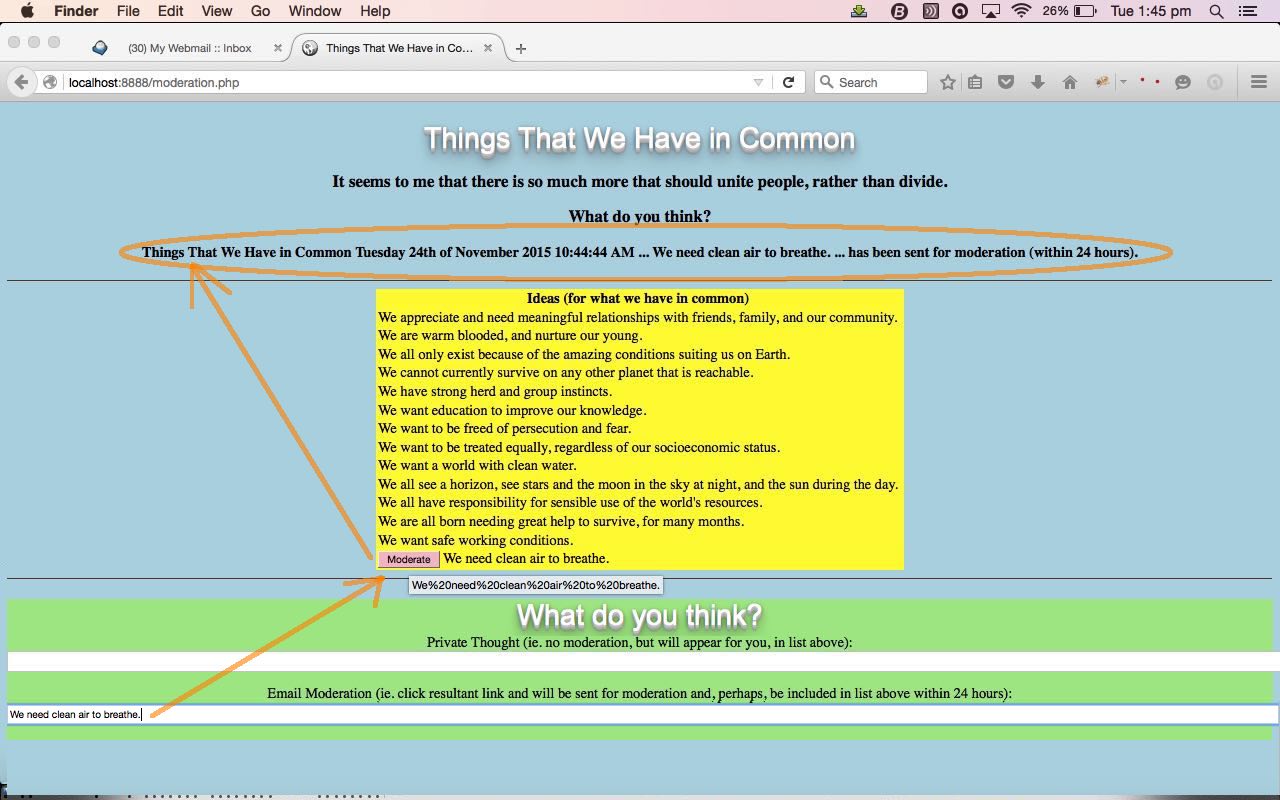
So, for the last time, today, we pose the idea that the “Things That We Have in Common” far outweigh the things that divide us, and present some ideas here. We offer, and encourage you to email us your ideas on the topic or use the file moderation method, and we’ll moderate them within 24 hours. With today’s file moderation method you are given the opportunity to login and “moderate” your own work but as you will recall from yesterday with …
CAPTCHA does not affect user roles going forward. In all these scenarios we present, where we don’t ask anything of you (ie. no registration), except an email address, presumably, you can be thought of as a …
- “guest” user … though in strict terms the word “guest” usually implies that there is a user registration involved … which we do not do here today … but to read a bit about this you could read PHP Membership Website Primer Tutorial … as distinct from …
- the emailee of the “guest” user will be an “admin” user … one who can offer the means to moderate the uploaded data, and, as approved, write that data to a place where it will be picked up and included in the contents of the webpage(s) involved … hence the term “Content Management System”
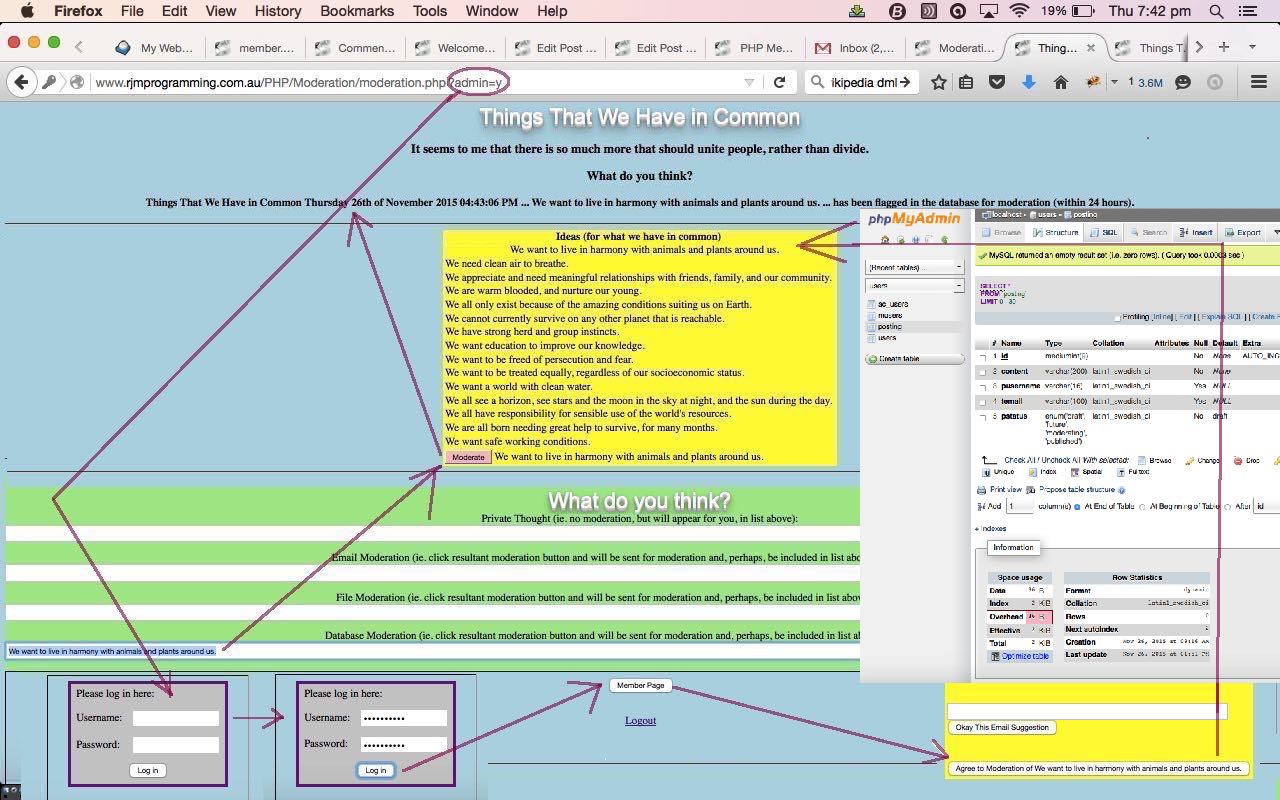
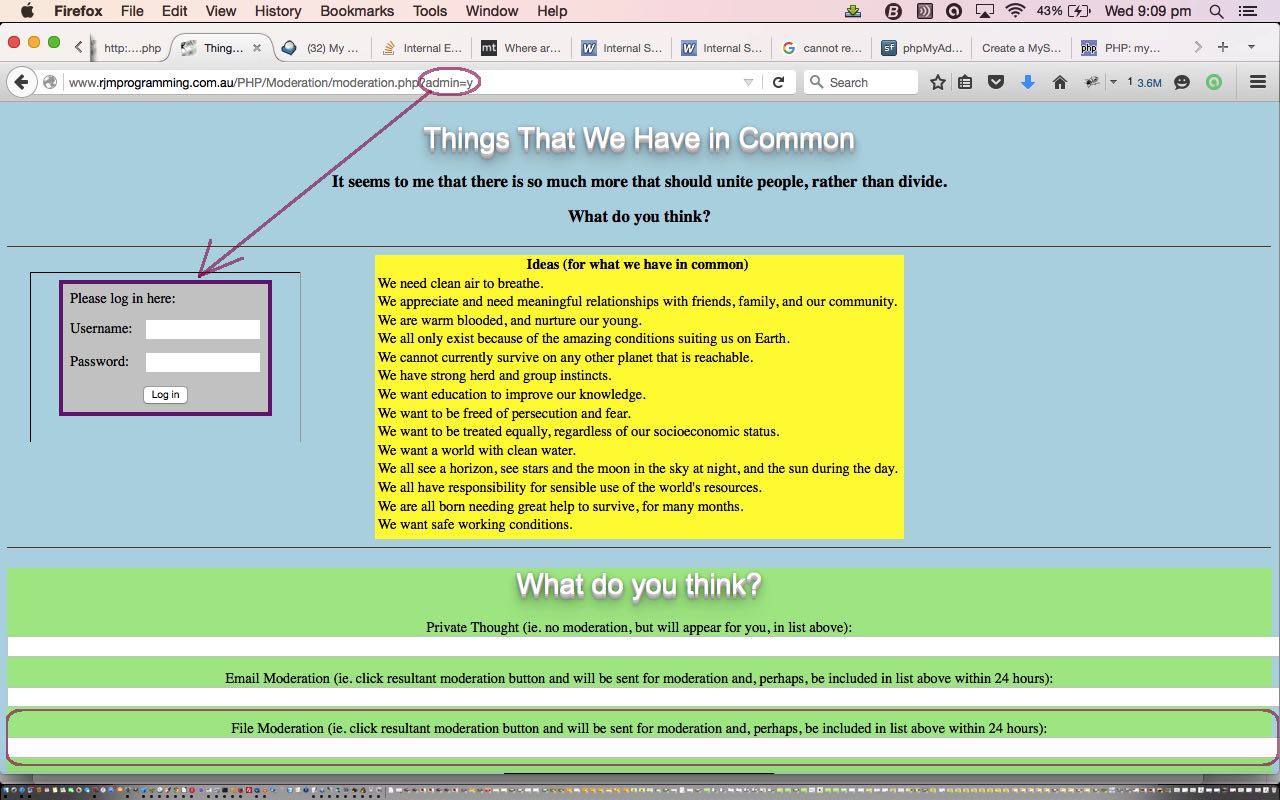
… you, as a “guest” user will not succeed with this “admin” user login to “moderate”, but the mechanism is there for real “admin” users, as is a “get” parameter method like our “?admin=y” idea, with most blogs and CMS websites.
Here is the downloadable PHP code you could call moderation_captcha.php with its live run and changed from yesterday’s work this way.
Here is the login PHP code for the admin section you could call login.php with its admin user useful live run, unchanged from yesterday.
Here is the PHP code login(.php) uses to connect to the MySql database you could call db_connect.php unchanged from yesterday.
Here is the member PHP code that follows the login(.php) page you could call member.php that handles, so far, the “business logic” for file moderation as of yesterday and the admin user follow up to reading the email and approving the email moderation, of two days back, as well as today’s extended MySql database functionality, is not needing to change from yesterday’s work regarding CAPTCHA.
Previous relevant Moderation by MySql Database Primer Tutorial is shown below.
Today’s the day we tackle some database “moderation” ideas. You will recall from yesterday’s Moderation by File Primer Tutorial as shown below, that “moderation” is associated with blogs and Content Management Systems and social media as a means by which uploaded content can be vetted, or not, during a “moderation phase” for a posting of some sort.
This can involve, in our eyes, quite a few options, none of which would not involve a server-side solution of some sort …
- no moderation … even this needs a server side language, in our eyes, because you will be changing a server side webpage for all users
- email (or sms or voicemail or any direct communication method) moderation … ask for an admin user of the website to change things after having emailed them … this is the one we showed two days back … and please feel free to try your own entries
- moderate via a (web server) database with posting statuses such as “Awaiting Moderation”, “Published”, “To Be Deleted” … this is the one we show today … and, yet again, please feel free to try your own entries
- moderate via a system of (web server) files with posting statuses such as “Awaiting Moderation”, “Published”, “To Be Deleted” … this is the one we showed yesterday … and, again, please feel free to try your own entries
- only moderate to either of the four above after having gone through a CAPTCHA test that the user is not a robot
So today we are still here posing the idea that the “Things That We Have in Common” far outweigh the things that divide us, and present some ideas here. We offer, and encourage you to email us your ideas on the topic or use the file moderation method, and we’ll moderate them within 24 hours. With today’s file moderation method you are given the opportunity to login and “moderate” your own work but as you will recall from yesterday with …
The major lesson today, for us, is to show you the brilliance of phpMyAdmin as the administrator back-end to a MySql database. Some of the great features of phpMyAdmin we used to get to this point are …
- phpMyAdmin’s great ability to export (to SQL, most usefully) the structure, in terms of “CREATE TABLE” type SQL and/or data of existant database tables as a useful way to help design your own new database tables
- phpMyAdmin’s ease of use of the usual DML SQL functionality
- phpMyAdmin’s ease of use of the usual DDL SQL functionality for the creation of users and the granting or denial of user priviledges, and drop and truncate functionalities
We still have the two basic web user roles going today. In this scenario, where we don’t ask anything of you (ie. no registration), except an email address, presumably, you can be thought of as a …
- “guest” user … though in strict terms the word “guest” usually implies that there is a user registration involved … which we do not do here today … but to read a bit about this you could read PHP Membership Website Primer Tutorial … as distinct from …
- the emailee of the “guest” user will be an “admin” user … one who can offer the means to moderate the uploaded data, and, as approved, write that data to a place where it will be picked up and included in the contents of the webpage(s) involved … hence the term “Content Management System”
… you, as a “guest” user will not succeed with this “admin” user login to “moderate”, but the mechanism is there for real “admin” users, as is a “get” parameter method like our “?admin=y” idea, with most blogs and CMS websites.
You will recall yesterday that ideas from PHP Membership Website Primer Tutorial came into play with the use of web server files and today its functionality is even more important with some MySql database work to follow up on phpMyAdmin database setup preparation. It screens “admin” users from the rest, ensuring you can write your fully functional database PHP free in the knowledge that the user is logged in as an “admin” user.
Here is the downloadable PHP code you could call moderation.php with its live run and changed from yesterday’s work this way.
Here is the login PHP code for the admin section you could call login.php with its admin user useful live run, unchanged from yesterday.
Here is the PHP code login(.php) uses to connect to the MySql database you could call db_connect.php unchanged from yesterday.
Here is the member PHP code that follows the login(.php) page you could call member.php that handles, so far, the “business logic” for file moderation as of yesterday and the admin user follow up to reading the email and approving the email moderation, of two days back, as well as today’s extended MySql database functionality, is changed from yesterday’s work this way.
Previous relevant Moderation by File Primer Tutorial is shown below.
We continue on with “moderation” ideas today, as with WordPress 4.1.1’s Moderation by File Primer Tutorial. You will recall from yesterday’s Moderation by Email Primer Tutorial as shown below, that “moderation” is associated with blogs and Content Management Systems and social media as a means by which uploaded content can be vetted, or not, during a “moderation phase” for a posting of some sort.
This can involve, in our eyes, quite a few options, none of which would not involve a server-side solution of some sort …
- no moderation … even this needs a server side language, in our eyes, because you will be changing a server side webpage for all users
- email (or sms or voicemail or any direct communication method) moderation … ask for an admin user of the website to change things after having emailed them … this is the one we showed yesterday … and please feel free to try your own entries
- moderate via a (web server) database with posting statuses such as “Awaiting Moderation”, “Published”, “To Be Deleted”
- moderate via a system of (web server) files with posting statuses such as “Awaiting Moderation”, “Published”, “To Be Deleted” … this is the one we show today … and, again, please feel free to try your own entries
- only moderate to either of the four above after having gone through a CAPTCHA test that the user is not a robot
So today we continue to pose the idea that the “Things That We Have in Common” far outweigh the things that divide us, and present some ideas here. We offer, and encourage you to email us your ideas on the topic or use the file moderation method, and we’ll moderate them within 24 hours. With today’s file moderation method you are given the opportunity to login and “moderate” your own work but as you will recall from yesterday with …
This brings up the topic of web user roles. In this scenario, where we don’t ask anything of you, except an email address, presumably, you can be thought of as a …
- “guest” user … though in strict terms the word “guest” usually implies that there is a user registration involved … which we do not do here today … but to read a bit about this you could read PHP Membership Website Primer Tutorial … as distinct from …
- the emailee of the “guest” user will be an “admin” user … one who can offer the means to moderate the uploaded data, and, as approved, write that data to a place where it will be picked up and included in the contents of the webpage(s) involved … hence the term “Content Management System”
… you, as a “guest” user will not succeed with this “admin” user login to “moderate”, but the mechanism is there for real “admin” users, as is a “get” parameter method like our “?admin=y” idea, with most blogs and CMS websites.
The reason we didn’t need these PHP Membership Website Primer Tutorial ideas yesterday was that no web server files had to be written at that stage, but today they do, and we can’t let any “guest” user do it, so we find that MySql database work via the wonderful and enormously stupendous phpMyAdmin comes into play, and we’ll talk more about this tomorrow, when databases are used for all aspects of our final “moderation” via database discussion.
Here is the downloadable PHP code you could call moderation.php with its live run and changed from yesterday’s work this way.
Here is the login PHP code for the admin section you could call login.php with its admin user useful live run.
Here is the PHP code login(.php) uses to connect to the MySql database you could call db_connect.php
Here is the member PHP code that follows the login(.php) page you could call member.php that handles, so far, the “business logic” for file moderation and the admin user follow up to reading the email and approving the email moderation, of yesterday.
Previous relevant Moderation by Email Primer Tutorial is shown below.
The term “moderation” is associated with blogs and Content Management Systems and social media as a means by which uploaded content can be vetted, or not, during a “moderation phase” for a posting of some sort.
This can involve, in our eyes, quite a few options, none of which would not involve a server-side solution of some sort. We’ll think on this further (maybe Ajax?!), but some of the ideas for moderation would be …
- no moderation … even this needs a server side language, in our eyes, because you will be changing a server side webpage for all users
- email (or sms or voicemail or any direct communication method) moderation … ask for an admin user of the website to change things after having emailed them … this is the one we show today … and please feel free to try your own entries
- moderate via a (web server) database with posting statuses such as “Awaiting Moderation”, “Published”, “To Be Deleted”
- moderate via a system of (web server) files with posting statuses such as “Awaiting Moderation”, “Published”, “To Be Deleted”
- only moderate to either of the four above after having gone through a CAPTCHA test that the user is not a robot
So today we pose the idea that the “Things That We Have in Common” far outweigh the things that divide us, and present some ideas here. We offer, and encourage you to email us your ideas on the topic, and we’ll moderate them within 24 hours. The mechanism, today, is via you, the user, sending us here, at RJM Programming, an email.
This brings up the topic of web user roles. In this scenario, where we don’t ask anything of you, except an email address, presumably, you can be thought of as a …
- “guest” user … though in strict terms the word “guest” usually implies that there is a user registration involved … which we do not do here today … but to read a bit about this you could read PHP Membership Website Primer Tutorial … as distinct from …
- the emailee of the “guest” user will be an “admin” user … one who can offer the means to moderate the uploaded data, and, as approved, write that data to a place where it will be picked up and included in the contents of the webpage(s) involved … hence the term “Content Management System”
… and so, in the scenario of “no moderation” “guest” users circumvent the moderation part of the “admin” user role and, in some automated (programming) way, with a language like PHP and a database like MySql, be able to get their uploaded content straight onto the webpage(s) of interest. So, sometimes you see “no moderation” but a CAPTCHA (robot) check, as the scenario of use.
Of interest, too, is the nature of the uploaded data. Is it “just text” or “can it contain images” or “can it contain videos” etcetera. Today, we are just allowing text.
Here is the downloadable PHP code you could call moderation.php with its live run.
If this was interesting you may be interested in this too.
If this was interesting you may be interested in this too.
If this was interesting you may be interested in this too.
If this was interesting you may be interested in this too.
If this was interesting you may be interested in this too.
If this was interesting you may be interested in this too.